LM393 Comparator Pinout, Working Principle and Circuit
Author:admin Date: 2025-03-10 08:26 Views:370
LM393 Comparator for Noobs (with test circuit)
The LM393 comparator is a widely used dual differential comparator that plays a crucial role in various electronic applications, such as voltage detection, zero-crossing detection, and sensor signal processing. This article provides a detailed overview of the LM393, covering its working principle, pin configuration, circuit design, and practical applications, including its integration with Arduino and microcontrollers.
What is LM393?
The LM393 is a dual differential comparator IC that compares two input voltages and provides a low-voltage digital output. Unlike operational amplifiers (op-amps), comparators like the LM393 are designed for fast switching between high and low states when the input voltage crosses a reference threshold.
LM393 Features
The LM393 is known for its reliable performance and flexibility in different circuit designs. Below are its key specifications:
- Supply Voltage: 2V to 36V (single supply) or ±1V to ±18V (dual supply)
- Low Power Consumption: 0.4mA per comparator
- Response Time: 300ns (fast switching)
- Open-Collector Output: Requires an external pull-up resistor
- Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
The open-collector output is particularly useful for applications where multiple comparators need to be connected to a common output line.
LM393 Pinout

The LM393 IC consists of two independent voltage comparators and features an 8-pin layout:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1OUT | Output of Operational Amplifier 1 |
| 2 | 1IN- | Inverting Input of Operational Amplifier 1 |
| 3 | 1IN+ | Non-Inverting Input of Operational Amplifier 1 |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
| 5 | 2IN+ | Non-Inverting Input of Operational Amplifier 2 |
| 6 | 2IN- | Inverting Input of Operational Amplifier 2 |
| 7 | 2OUT | Output of Operational Amplifier 2 |
| 8 | VCC | Power Supply |
LM393 Working Principle: How It Works?
The LM393 comparator operates by comparing the voltages at its inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) inputs:
- If V+ > V-, the output remains HIGH (open-collector state).
- If V- > V+, the output switches to LOW (sinking current to ground).
Key Considerations:
- The output is open-collector, meaning it needs a pull-up resistor (e.g., 10kΩ) to function properly.
- The LM393 does not amplify signals like an op-amp—it only switches states.
LM393 Application Examples
The LM393 is found in various electronic applications, including:
- Zero-Crossing Detector: Identifies the point where an AC signal crosses zero volts, useful for phase detection.
- Overvoltage & Undervoltage Protection: Used in power supply circuits to detect voltage anomalies.
- Battery Level Monitoring: Compares battery voltage against a preset reference voltage.
- IR Sensors & Light Detectors: Converts light sensor outputs into digital signals for microcontroller interfacing.
- PWM Signal Processing: Used in switching circuits and waveform shaping.
LM393 Circuit Design
LM393 Circuit Diagram:
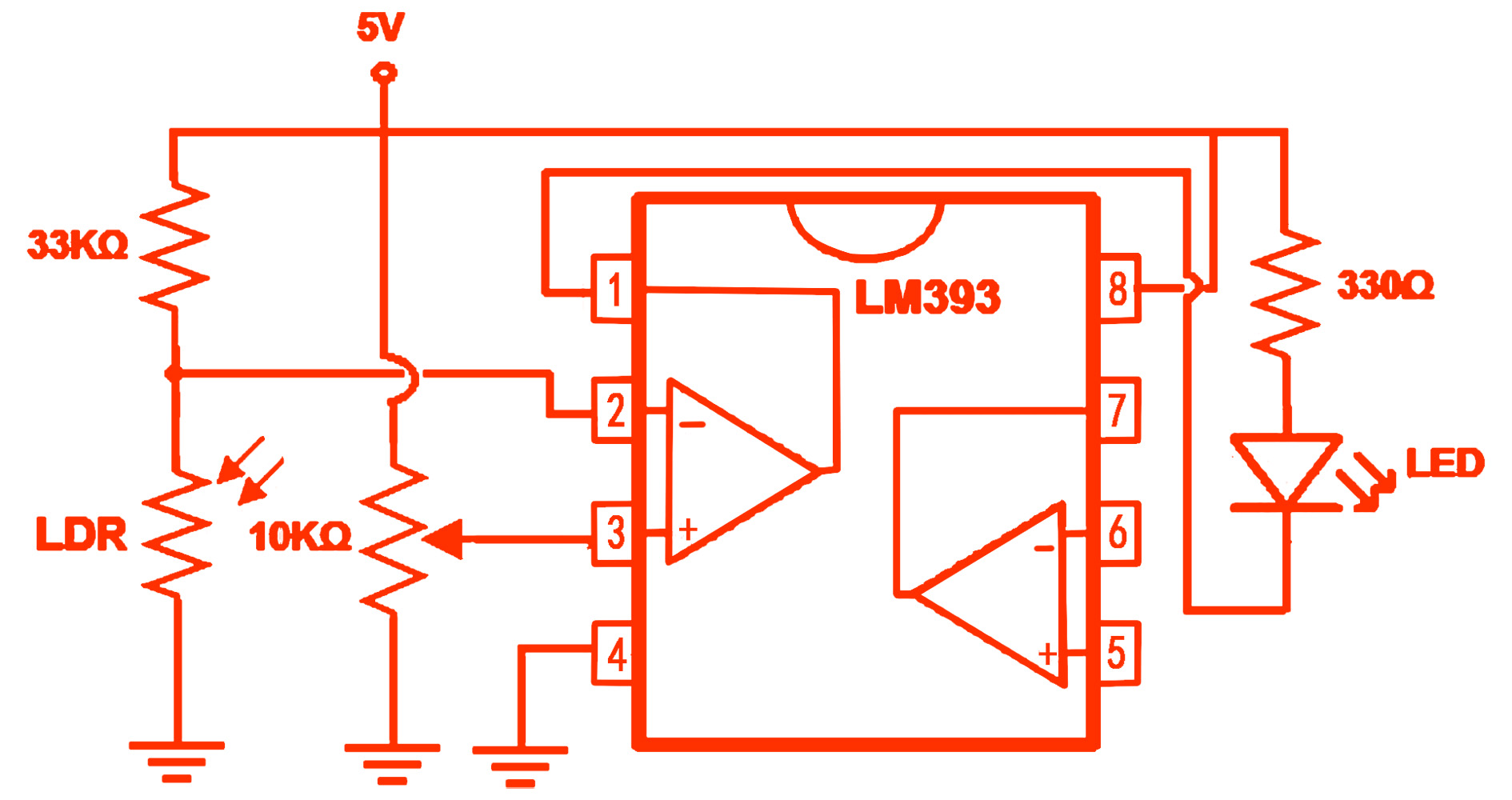
Components:
- LM393
- LDR
- 10kΩ Resistor
- 33kΩ Resistor
- LED
- Power Supply (5V)
Description:
This is a light-sensitive voltage comparator circuit using an LM393 comparator IC. The LDR and the 10kΩ resistor form a voltage divider that provides a varying voltage to the non-inverting input (Pin 3) of the LM393. A reference voltage is set at the inverting input (Pin 2) using the 33kΩ resistor.
LM393 with Arduino

The LM393 comparator can be easily interfaced with Arduino, ESP32, or Raspberry Pi for various sensor-based applications.
LM393 Arduino Library
For Arduino users, the LM393 does not require a special library—you can directly read its digital output using the digitalRead() function.
LM393 Arduino Project: Light Sensor
Objective: Detect light intensity using an LDR sensor and LM393.
Connections:
- LDR Sensor → LM393 Input
- LM393 Output → Arduino Digital Pin
- LED Indicator (Optional)
Arduino Code Example:

This code reads the LM393 output and displays the HIGH/LOW signal in the Serial Monitor.
LM393 Equivalent
If LM393 is unavailable, you can use alternative comparators like:
| Model | Manufacturer | Type | Operating Voltage Range | Response Time | Output Current (Sink) | Package Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM393 | Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, STMicroelectronics | Dual Comparator | 2V – 36V | 1.3µs | 16mA | SOIC-8 |
| LM2903 | Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, STMicroelectronics | Dual Comparator | 2V – 36V | 1.3µs | 16mA | SOIC-8 |
| LM339 | Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, STMicroelectronics | Quad Comparator | 2V – 36V | 1.3µs | 16mA | SOIC-14 |
| UA393 | Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor | Dual Comparator | 2V – 36V | 1.3µs | 16mA | SOIC-8 |
LM339 is the closest alternative, as it has four comparators instead of two.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting LM393
If your LM393 circuit is not working properly, check the following:
- Incorrect Pull-up Resistor – Without a pull-up resistor, the output may not function.
- Floating Input Pins – Unconnected inputs can cause erratic behavior.
- Insufficient Voltage Supply – Ensure VCC is within the 2V-36V range.
- Incorrect Reference Voltage – Adjust the voltage divider correctly.
LM393 Package

The LM393 comparator is available in DIP and SMD packages for different PCB designs.
Conclusion
The LM393 is an essential comparator IC for voltage detection, sensor interfacing, and power management. With its low power consumption, wide voltage range, and open-collector output, it remains a versatile choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does an LM393 Comparator cost?
The price of the LM393 Comparator varies by manufacturer and quantity purchased. Typically, prices range from $0.10 to $1.00 per unit, while retail prices may be slightly higher.
How to prevent false triggering in LM393 circuits?
Use hysteresis (100kΩ–1MΩ feedback resistor), input capacitors, and a stable reference voltage.
Where can I find the LM393 datasheet?
You can find the LM393 datasheet on our official website for complete specifications, pin assignments and electrical characteristics.


