LM386 Op Amp Pinout, Works and Circuits
Author:admin Date: 2025-04-03 06:44 Views:208
How to make an LM386 audio amplifier circuit
The LM386 Op Amp is a low-voltage audio power amplifier IC that is incredibly popular in audio electronics. From hobby projects to commercial devices, the LM386 is known for its simplicity, efficiency, and ease of use. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the LM386 Op Amp, including its pinout, how it works, internal schematic, popular circuit designs, and even alternatives.
What is LM386?
The LM386 is a power amplifier designed specifically for audio applications. It is used to increase the amplitude of weak audio signals and drive small speakers. One of the biggest advantages of the LM386 is that it doesn’t require a lot of external components. This makes it perfect for beginners, prototyping, and compact applications.
Unlike general-purpose operational amplifiers, the LM386 is designed to deliver enough power to drive a speaker directly. It’s not just a preamp—it’s a full mini power amplifier. Despite its small size, it can output around 0.325W of audio power into an 8-ohm load when powered with a 6V supply.
LM386 Features
Here are the key features that make LM386 ideal for low-power audio applications:
Operating Voltage: 4V to 12V (LM386N supports up to 18V)
Quiescent Current: Only 4mA, ideal for battery-powered devices
Gain: Internally fixed at 20, can be increased to 200 with a capacitor between Pins 1 and 8
Output Power: Around 0.325W at 6V with 8-ohm speaker
Frequency Response: 300 Hz to 100 kHz
THD (Total Harmonic Distortion): Less than 1%
Compact 8-pin DIP/SOIC package
Built-in bypass pin for noise reduction
No need for heatsink in most applications
These features make LM386 suitable for portable radios, small audio speakers, toys, intercoms, and more.
LM386 Pinout
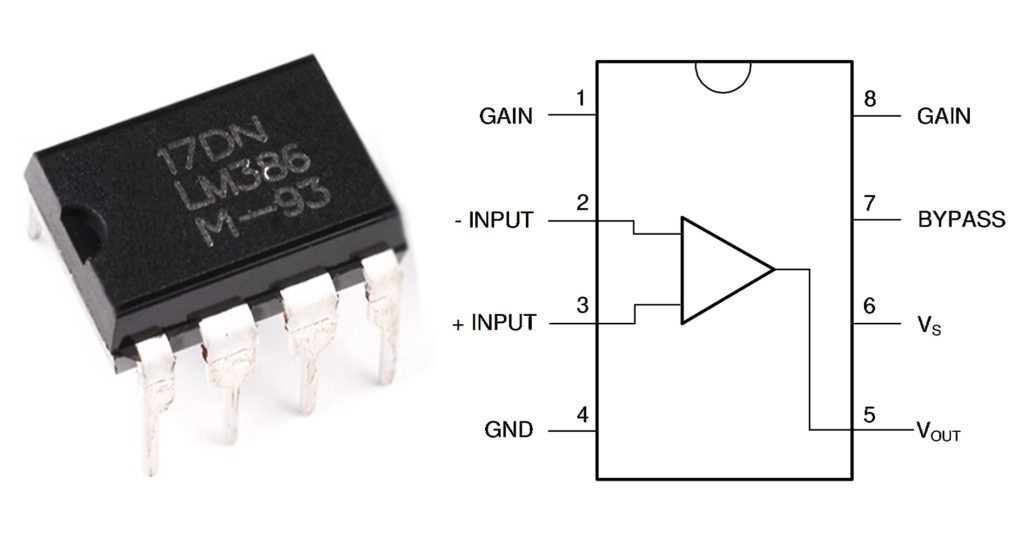
Understanding the LM386 pinout is essential before wiring it up in a circuit. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GAIN | Gain control pin |
| 2 | – INPUT | Inverting input |
| 3 | + INPUT | Non-inverting input |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
| 5 | VOUT | Output |
| 6 | VS | Supply voltage |
| 7 | BYPASS | Bypass capacitor pin |
| 8 | GAIN | Gain control pin |
Gain Control
By default, the gain is set to 20. Connecting a capacitor between pins 1 and 8 allows you to increase the gain up to 200. This makes the IC highly adaptable depending on the level of amplification you need.
LM386 Working Principle
How Does the LM386 Work?
The LM386 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier that boosts weak audio signals to drive small speakers or headphones.
Audio Input:
The input signal is applied to the non-inverting input (Pin 3), while the inverting input (Pin 2) is grounded.
Gain Control:
The default gain is 20. Connecting a capacitor between Pin 1 and Pin 8 increases the gain up to 200.
Amplification:
The internal amplifier stages apply the gain, increasing the signal’s amplitude.
Output Stage:
The amplified signal is sent through Pin 5 to a connected speaker, typically via a coupling capacitor to block DC.
Power Supply and Noise Control:
The LM386 operates on 4V to 12V through Pin 6, and a bypass capacitor on Pin 7 can reduce noise.
This efficient design makes the LM386 ideal for portable speakers, radios, and DIY audio projects.
LM386 Circuit Design

When designing an LM386 circuit, consider the following factors to ensure optimal performance:
Power Supply Voltage:
1. Operates within 4V to 12V (up to 18V for some models).
2. Use decoupling capacitors (0.1µF and 100µF) near Pin 6 for noise reduction.
Gain Control:
1. Default gain is 20; add a 10µF capacitor between Pins 1 and 8 to increase it to 200.
2. Higher gains may introduce noise; use bypass capacitors to minimize it.
Speaker Impedance:
1. Best suited for 8Ω speakers.
2. Lower impedance may overheat the IC, while higher impedance reduces output power.
Noise Reduction:
1. Add a 0.1µF capacitor from Pin 7 to ground to reduce noise.
2. Keep input and output traces short to minimize interference.
Heat Management:
1. No heatsink required for typical use.
2. Ensure proper ventilation for continuous high-output applications.
Volume and Tone Control:
1. Use a 10kΩ to 100kΩ potentiometer for volume adjustment.
2. Add simple RC filters for tone control if needed.
Circuit Protection:
1. Include a reverse polarity protection diode and a fuse for safer operation.
2. Following these guidelines will help you create efficient and reliable LM386 circuits for your audio applications.
LM386 Applications
The LM386 is a low voltage audio power amplifier commonly used in various applications due to its simplicity, low cost, and efficiency.
Portable Audio Amplifiers:
Used in small speaker systems, battery-operated devices, and audio playback modules.
Intercoms and Communication Devices:
Ideal for intercom systems, two-way communication devices, and voice recording units.
Sound Effects Circuits:
Integrated into sound effect generators, musical toys, and educational devices.
Microphone Preamplifiers:
Amplifies low-level signals from microphones for voice amplification and audio processing.
Audio Test Equipment:
Used in small-scale testing devices to evaluate speaker output and circuit functionality.
Hearing Aids and Assistive Devices:
Suitable for assistive listening devices due to its low power consumption.
The LM386’s versatility makes it a popular choice in both commercial and DIY electronics projects.
Pros and Cons of LM386
Pros:
1. Simple and easy to use with minimal external components.
2. Low power consumption, ideal for battery-powered devices.
3. Adjustable gain (20 to 200) with a single capacitor.
4. Compact 8-pin package for small projects.
5. Directly drives small speakers without extra components.
Cons:
1. Limited output power (0.325W), unsuitable for large speakers.
2. Can introduce noise or distortion at high gain.
3. Not suitable for high-fidelity audio.
4. May overheat under continuous high-load use.
5. Mono output only, requiring two ICs for stereo applications.
The LM386 is a great choice for small, low-power audio applications but may not be ideal for high-quality or high-power sound systems.
LM386 Equivalent and Alternative ICs
While the LM386 is a versatile and reliable audio amplifier IC, there are several alternatives available if you need more power, better efficiency, or additional features. Here are some common LM386 equivalents and alternatives to consider:
| Picture | Name | Type | Power Output | Supply Voltage | Key Features | Package |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
TDA2822 | Dual Audio Amplifier | 1W per channel | 3V to 15V | Supports stereo output, low cost | DIP-8, SOP-8 |
 |
PAM8403 | Class-D Audio Amplifier | 3W per channel | 2.5V to 5.5V | High efficiency, digital amp | SOP-16 |
 |
TDA7052 | Mono Audio Amplifier | 1W | 3V to 18V | No external components needed for output | DIP-8, SO-8 |
 |
LM380 | Audio Power Amplifier | 2W | 10V to 22V | Higher power than LM386 | DIP-14, TO-220-14 |
Choosing the Right Alternative
1. For Higher Power Output: If you need more than the 0.325W output of LM386, consider TDA2822 or LM380.
2. For Battery-Powered Devices: The PAM8403 is a more efficient Class-D amplifier, consuming less power and producing less heat.
3. For Stereo Audio: The TDA2822 offers stereo capability with simple circuitry.
4. For Simple Applications: The TDA7052 is an easy-to-use amplifier with minimal external components, suitable for toys or voice amplification.
While the LM386 remains an excellent choice for low-power, analog audio amplification, these alternatives provide specialized solutions for more demanding applications.
LM386 Package Types
SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit):
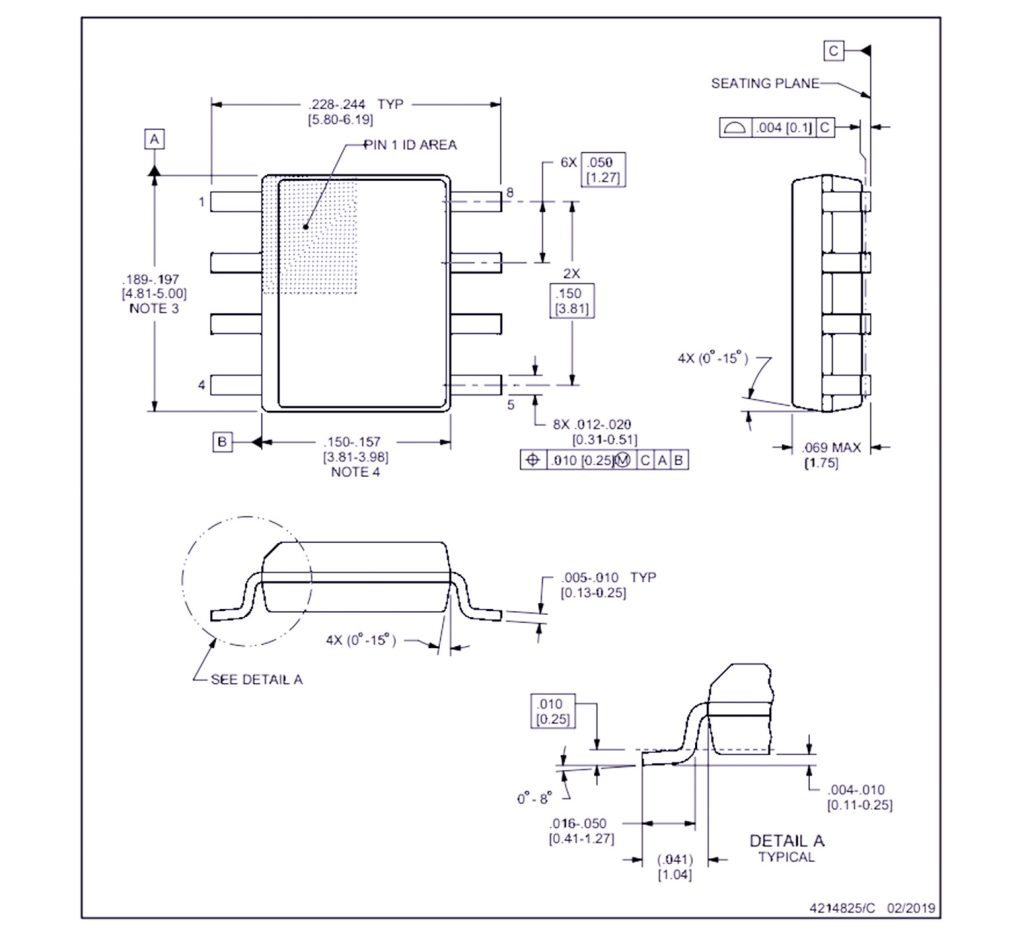
The SOIC package is a surface-mount package with gull-wing leads, typically used in compact and lightweight designs. It offers excellent electrical performance and is widely used in consumer electronics and portable audio devices. The small footprint makes it ideal for applications where space is limited.
P (R-PDIP-T8):

The R-PDIP-T8, also known as the Plastic Dual In-line Package with 8 pins, is a traditional through-hole package. It provides robust mechanical strength and is easy to handle during manual assembly or prototyping. This package is preferred in applications requiring reliable connections and simple PCB design.
VSSOP (Very Thin Shrink Small Outline Package):

The VSSOP is an ultra-compact surface-mount package designed for high-density circuit boards. Its thin and small form factor is advantageous for space-constrained applications like portable speakers, hearing aids, and battery-operated devices. Despite its size, it ensures efficient thermal management and reliable performance.
Conclusion
The LM386 op amp is a compact and practical solution for small audio amplification. Whether you’re building a DIY speaker, a miniature guitar amplifier, or learning electronics for the first time, the LM386 strikes a balance between performance and simplicity. By understanding the LM386 pinout, how it works, and how to build circuits with it, you can easily integrate it into a variety of projects.
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is LM386 a Class AB Amplifier?
Yes, the LM386 is a Class AB amplifier, offering low distortion and improved efficiency compared to Class A while reducing the crossover distortion seen in Class B designs.
2. What is the Price of LM386?
The price of the LM386 varies depending on the supplier, quantity, and packaging type. Generally, it ranges from $0.30 to $2 per unit for small quantities, with bulk purchases offering significant discounts.
3. Where Can I Find the LM386 Datasheet?
You can find the LM386 datasheet on our website. The datasheet provides detailed information on pin configuration, electrical characteristics, application circuits, and design recommendations.
4. How Do I Make a Simple LM386 Audio Amplifier?
To make a simple LM386 audio amplifier, connect pin 6 to a 4V to 12V power supply, pin 4 to ground, and pin 3 to the audio input through a 0.1µF capacitor. Connect an 8-ohm speaker to pin 5 through a 220µF capacitor. Optionally, add a 10µF capacitor between pins 1 and 8 to increase the gain to 200.