TP4057 schematic & datasheet | vs TP4056 EVVO
- Battery Chemistry: Lithium Ion
- Charge Current - Max: 500mA
- Current - Charging: Constant - Programmable
- Package: SOT-23-6

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
TP4056 vs. TP4057 Li-Ion Battery Charging Boards Quick Comparison 18650 And More
TP4056 vs TP4057
Differences between TP4056 VS TP4057 in Pin Configuration and Application Circuits:
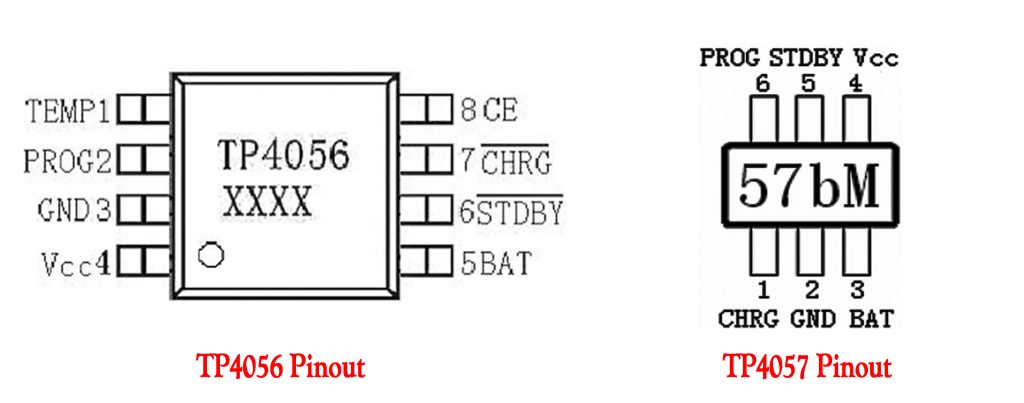
| Comparison Item | TP4056 (SOP-8 Package) | TP4057 (SOT23-6 Package) |
|---|---|---|
| Chip Pins | 8-pin Package ① TEMP (Temperature sensing input) ② PROG (Charge current setting) ③ GND (Ground) ④ VCC (Power input) ⑤ BAT (Battery positive terminal) ⑥ STDBY (Charge complete indicator) ⑦ CHRG (Charging status indicator) ⑧ CE (Chip enable control) |
6-pin Package ① CHRG (Charging status indicator) ② GND (Ground) ③ BAT (Battery positive terminal) ④ VCC (Power input) ⑤ STDBY (Charge complete indicator) ⑥ PROG (Charge current setting) |
| Pin Differences Summary | Includes additional TEMP pin for temperature sensing. CE pin available for external control to enable/disable the chip. |
No TEMP pin for temperature sensing. No CE pin; chip is always enabled. |
| Application Circuit Differences | More complex; supports NTC thermistor (connected to TEMP pin) for battery temperature monitoring. Includes additional enable/disable functionality (via CE pin). |
Simpler; no temperature monitoring function, ideal for compact and space-constrained designs. |
| Maximum Charge Current | Up to 1A | Recommended maximum of 500mA |
| Charge Current Setting Formula | ICHG = 1200 / RPROG | ICHG = 1000 / RPROG |
| Typical Rprog Selection | 1.2kΩ resistor for 1A charge current | 2kΩ resistor for approximately 500mA charge current |
TP4056 VS TP4057 peripheral circuits, specific pin connections, and functions of each external component:

| Component | TP4056 Peripheral Circuit (Left Diagram) | TP4057 Peripheral Circuit (Right Diagram) |
|---|---|---|
| Input Current-Limiting Resistor | RL1 = 0.4Ω, connected to VCC (Pin 4) Limits input surge current to protect the chip from potential damage. |
Not Present (5V input directly to VCC, Pin 4) |
| Input Filter Capacitor | C1 = 10μF, connected between VCC (Pin 4) and GND (Pin 3) Reduces ripple noise and stabilizes input voltage. |
1μF, connected between VCC (Pin 4) and GND (Pin 2) Basic noise filtering for compact designs. |
| Output Filter Capacitor | C2 = 10μF, connected between BAT (Pin 5) and GND (Pin 3) Ensures stable battery voltage and reduces output ripple. |
10μF, connected between BAT (Pin 3) and GND (Pin 2) Same function: stabilizes battery voltage during charging. |
| Charging Status LEDs and Resistors | Two LEDs: – D1 with RL2=1kΩ resistor, connected to CHRG (Pin 7): indicates charging status. – D2 with RL3=1kΩ resistor, connected to STDBY (Pin 6): indicates charging completed or standby mode. |
Single LED with 1kΩ resistor connected to CHRG (Pin 1) Simplified indicator for charging status only. |
| Charge Current Setting Resistor (Rprog) | Rprog resistor connected between PROG (Pin 2) and GND (Pin 3) Determines charging current, e.g., 1.2kΩ sets approx. 1A. |
Rprog = 1.66kΩ, connected between PROG (Pin 6) and GND (Pin 2) Sets charging current around 600mA. |
| Temperature Sensing Resistor (NTC) | RL4 (10kΩ or NTC thermistor) connected between TEMP (Pin 1) and GND (Pin 3) Monitors battery temperature for enhanced safety during charging. |
No Temperature Sensing Capability |
| Chip Enable Control (CE Pin) | CE (Pin 8): external control signal Allows enabling or disabling the chip. |
No Enable Control Pin Chip always enabled by default. |
TP4056 Peripheral Circuit (Left Diagram):
1. More complex; includes temperature sensing, dual LED status indicators, input current limiting, and enable control.
2. Ideal for applications requiring higher safety and additional functionality.
TP4057 Peripheral Circuit (Right Diagram):
3. Simpler design; fewer external components, no temperature monitoring, single LED indicator, and always-on operation.
4. Ideal for compact, low-current, straightforward applications.