SB330 | Datasheet, Price, PDF onsemi
- Voltage-DCReverse(Vr)(Max): 30 V
- Current-AverageRectified(Io): 3A
- Voltage-Forward(Vf)(Max)@If: 500 mV @ 3 A
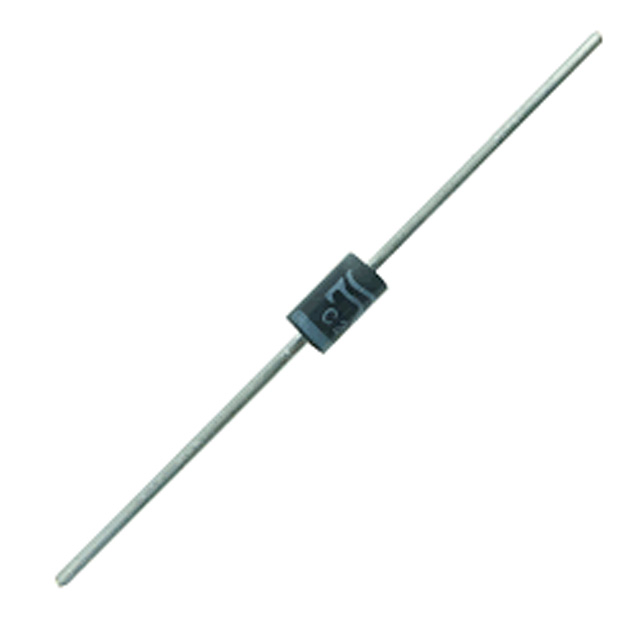
- Package: DO-201AD, Axial

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
sb330
The SB330 diode is a Schottky Barrier Diode, a type you’ll often see in power electronics. If you’re setting it up, you’ll appreciate its standard DO-201AD package—it’s straightforward to mount and does a good job managing heat.
You’ll find this diode especially useful for low-voltage situations since it has a maximum reverse voltage rating of 30 volts. Another plus is that it handles continuous forward currents up to 3 amps comfortably, which means it can support decent load requirements.
One thing you’ll definitely like is its low forward voltage drop—around 0.5 volts—so it wastes less energy and keeps efficiency high. It’s also quick when it comes to switching, making it ideal for circuits that operate at higher frequencies, such as switching power supplies or DC-DC converters.
With a broad working temperature range from -55°C up to 125°C, the SB330 diode is dependable in various environments. You’ll see it frequently used in battery chargers, inverters, and similar efficient applications.
sb330 pinout and polarity

| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description | Polarity Marking |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cathode (K) | Current output, negative terminal | Marked end with color ring on diode body |
| 2 | Anode (A) | Current input, positive terminal | Opposite end without color ring marking |
When you’re working with an SB330 diode, first look at the diode body—there’s usually a colored band or marking on one side, which shows you the cathode (negative side). The other end, without a mark, is the anode (positive side). Remember, current flows from the anode to the cathode during normal operation.
Always double-check the diode’s orientation when installing it into your circuit. Connecting it the wrong way won’t just keep your circuit from working—it could actually damage the diode itself.
Another thing to keep in mind: the maximum reverse voltage rating for the SB330 is 30 volts. Make sure your design never exposes the diode to higher reverse voltages, or you’ll risk damaging it.
Also, because this diode can generate some heat when handling higher currents, you should plan for proper heat dissipation. Good thermal management helps ensure stable operation and significantly extends the diode’s lifespan.
sb330 equivalent schottky diode





| Parameter | SB330 | 1N5821 | 1N5822 | SR330 | MBR330 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | 30V | 30V | 40V | 30V | 30V |
| Max Forward Current (IF) | 3A | 3A | 3A | 3A | 3A |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF, Typical) | 0.5V | 0.5V | 0.5V | 0.5V | 0.5V |
| Package Type | DO-201AD | DO-201AD | DO-201AD | DO-201AD | DO-201AD |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55~125°C | -55~125°C | -55~125°C | -55~125°C | -55~125°C |
When you’re choosing a replacement for your SB330 diode, always double-check that the substitute has a maximum reverse voltage and forward current rating that’s equal to or better than the original. This helps prevent unexpected circuit failures.
Also, it’s best if you select a replacement diode with the same DO-201AD package—that way you won’t have trouble installing it directly into your existing setup.
Lastly, take another look at your circuit’s cooling situation. Make sure the replacement diode can handle heat as effectively—or even better—than the SB330, ensuring reliable performance and a longer component life.
sb330 rectifier diode circuit

In this bridge rectifier circuit, you’re using four SB330 Schottky diodes (labeled D1 to D4) to convert AC voltage into pulsating DC. During the positive half of the AC cycle, diodes D1 and D2 turn on, allowing current to flow through your load in one direction. During the negative half, D3 and D4 conduct, again providing current in the same direction. The result? You get a smooth, one-way DC output. SB330 diodes are great here because they’re efficient, have a low voltage drop, and minimize energy loss, making them ideal for power supply and rectification tasks.
sb330 for reverse polarity protection
Using an SB330 diode for reverse polarity protection is a simple trick to safeguard your electronics from accidental power reversal. Just connect the diode in series with your power line. When the polarity is correct, the diode allows current to flow normally, with only about a 0.5V drop across it. If you hook up the power backwards, the diode quickly blocks current flow, protecting your device from damage. Just make sure your supply voltage stays below 30V (SB330’s maximum reverse rating) to avoid problems. And if you’re handling higher currents, don’t forget adequate cooling. You’ll find this method reliable and cost-effective in sensors, instruments, chargers, and various DC-powered devices.
sb330 fast recovery characteristics
The SB330 diode is great because of its fast recovery characteristics. Unlike regular diodes, it’s built using Schottky technology, meaning it switches super fast—usually less than 10 nanoseconds. This quick response reduces switching losses and helps your circuits run more efficiently, especially when you’re dealing with high-frequency setups like DC/DC converters, inverters, or PWM circuits. However, always keep your voltage under its 30V rating to avoid damage. Also, at high frequency and current, it can heat up, so good cooling is important. Overall, it’s perfect when you need reliable, efficient performance in high-speed rectification and protection circuits.
sb330 diode for switching power supply
When you’re building a switching power supply, the SB330 diode offers some real advantages. It has a very low forward voltage drop (about 0.5V), reducing wasted energy and boosting efficiency. Plus, its fast recovery time (under 10ns) helps cut down switching losses and EMI noise in high-frequency circuits. Rated at 3A, it’s perfect for medium or smaller power applications and stays stable from -55°C to 125°C.
You’ll typically see SB330 diodes used for output rectification in buck converters, as freewheeling diodes to manage voltage spikes, or placed near MOSFETs and IGBTs to protect them from sudden voltage surges.
sb330 vs ss34 performance
| Parameter | SB330 | SS34 | Comparison Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | 30V | 40V | SS34 has higher voltage endurance, suitable for a wider range of applications. |
| Max Forward Current (IF) | 3A | 3A | Both have identical rated currents. |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF, Typical) | Approx. 0.5V (at 3A) | Approx. 0.5V (at 3A) | Similar forward voltage drop, efficiency, and power dissipation. |
| Reverse Recovery Time (Trr) | Very short (<10ns) | Very short (<10ns) | Both use Schottky structure, offering excellent switching performance. |
| Package Type | DO-201AD (Axial) | SMA (SMD) | SB330 axial type is suitable for traditional welding, SS34 SMD type is optimized for automated SMT processes. |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to +125°C | -55°C to +125°C | Identical temperature performance. |
| Typical Applications | Axial type suitable for plug-in soldering and manual welding or repair. | SMD type suitable for automated mass production, saving PCB space. | Select based on packaging and production requirements. |
When you’re deciding between the SB330 and the SS34 diode, here’s a quick tip: If your circuit voltage stays under 30V, the SB330 will handle it perfectly fine. The SS34 offers slightly higher voltage tolerance if you need more headroom. Both have the same current rating and similar efficiency, so performance-wise, there’s hardly a difference. If you’re planning to solder by hand or using through-hole components, the SB330 is your go-to choice. But if you’re designing a compact PCB or using automated surface-mount assembly, you’ll prefer the SS34. Both switch fast, ideal for high-frequency rectification or freewheeling circuits. Choose according to your specific layout and assembly method.
sb330 application in dc-dc converter
If you’re working with DC-DC modules, the SB330 diode is your friend. In buck converters, it’ll act as a freewheeling diode, providing a safe path for current when your MOSFET switches off, stabilizing your output. You’ll see this in Arduino power modules, lithium battery regulators, or automotive power supplies. In boost circuits, SB330 efficiently rectifies pulses to stable DC, perfect for LED drivers or solar charging modules. In flyback circuits, it swiftly rectifies transformer outputs for adapters or isolated supplies. Also, it’s ideal as a protection diode in relay or motor drivers, saving your components from harmful voltage spikes.