LL4148 Diode | Datasheet | SMD Diode | Price MDD
- Voltage-DCReverse(Vr)(Max): 75 V
- Current-AverageRectified(Io): 200mA
- Voltage-Forward(Vf)(Max)@If: 1 V @ 50 mA
- Package: DO-213AC, MINI-MELF, SOD-80

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
Ll4148
If you’re designing circuits that involve high-frequency signals or quick switching, the LL4148 diode is a smart pick. It’s a small, surface-mount diode (SMD) in a compact SOD-80 glass package—perfect if your board space is tight. You’ll appreciate its super-fast switching speed (less than 4 ns), meaning less distortion and better signal integrity. It handles continuous currents up to 150 mA, ideal for low-current signal paths, and its 75 V reverse voltage rating covers most basic switching and protection needs. With a low forward voltage drop of about 0.72 V, it also helps keep power consumption down, making it popular in consumer electronics, communications, and computer circuits.
Ll4148 Pinout and Polarity
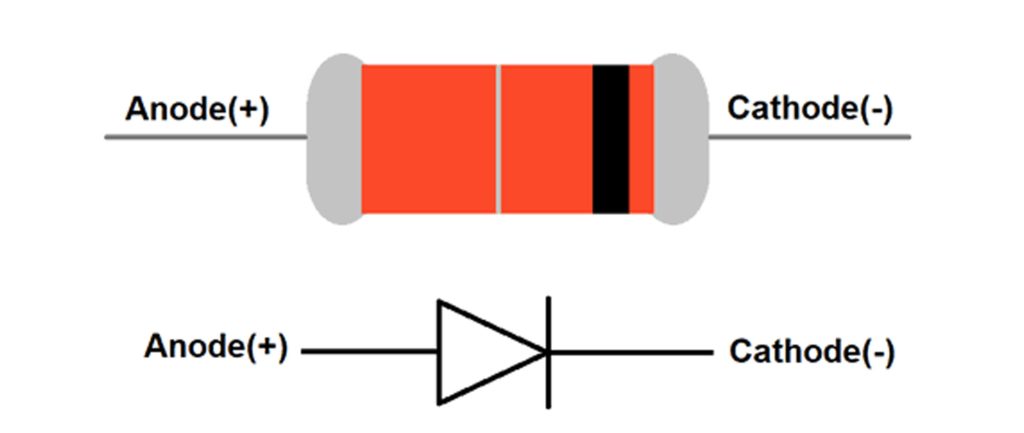
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cathode | Negative terminal of the diode, typically marked with a black band |
| 2 | Anode | Positive terminal of the diode, typically unmarked side |
When you’re using the LL4148 diode, one thing you’ve really got to watch out for is polarity—mixing up the anode and cathode can stop your circuit from working. On the LL4148 in the small SOD-80 package, you’ll see a black ring marking the cathode end, while the anode side stays unmarked. Always double-check this marking before soldering, because reversing it could cause trouble. Also, if you’re working with high-frequency or fast-switching circuits, keep your diode connections as short as possible. Shorter leads mean less unwanted inductance and capacitance, giving you cleaner signals and better overall performance.
Ll4148 Equivalent Diode Smd
| Parameter | LL4148 | BAV103 | 1N4448 | MMBD4148 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Package Type | SOD-80 (Glass) | SOD-80 (Glass) | SOD-80 (Glass) | SOT-23 (Plastic) |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage (VR) | 75 V | 200 V | 100 V | 75 V |
| Forward Current (IF) | 150 mA | 250 mA | 150 mA | 200 mA |
| Recovery Time (trr) | 4 ns | 50 ns | 4 ns | 4 ns |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF) | Approx. 0.72 V | Approx. 1.0 V | Approx. 0.72 V | Approx. 0.9 V |
When you’re looking to replace the LL4148 diode, here’s what you need to keep in mind. First, double-check the reverse voltage rating—your replacement diode must handle the voltage you’re working with. For instance, the BAV103 can handle up to 200V, great if your circuit has higher voltage demands. Also, ensure the diode’s forward current rating matches or exceeds your original diode; the BAV103 and MMBD4148 usually offer slightly better current capacity. If your circuit needs fast switching, choose replacements like 1N4448 or MMBD4148, as their speeds closely match LL4148. Lastly, remember the packaging—BAV103 and 1N4448 match the LL4148’s package, making them easy drop-in replacements. The MMBD4148, however, uses a SOT-23 package, so you’ll likely need to adjust your PCB layout.
Ll4148 Switching Diode Circuit

Here’s what’s happening in this circuit: when your GPIO pin goes high, it turns on the LED2 indicator and also powers the internal LED inside the TLP293GB optocoupler through resistor R10. Once the optocoupler activates, its transistor side lets current flow, providing bias current to the S8050 transistor (Q1). This then energizes your relay coil (K1), switching your connected load on or off.
Pay special attention to the LL4148 diode (D2)—it’s critical to install it correctly, as it absorbs voltage spikes from the relay coil when switching off, protecting your transistor. Also, ensure your 5V power supply can deliver enough current to reliably activate the relay. The optocoupler keeps your GPIO safely isolated from the relay side, preventing electrical interference and keeping everything running smoothly.
Ll4148 Vs 1n4148
| Parameter | LL4148 | 1N4148 |
|---|---|---|
| Package Type | SOD-80 (Glass SMD) | DO-35 (Glass Through-hole) |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage (VR) | 75 V | 100 V |
| Maximum Continuous Forward Current (IF) | 150 mA | 200 mA |
| Peak Forward Current (IFM) | 500 mA | 450 mA |
| Maximum Recovery Time (trr) | 4 ns | 4 ns |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF) | ~0.72 V | ~0.72 V |
| Power Dissipation (Pd) | 500 mW | 500 mW |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C ~ +150°C | -65°C ~ +175°C |
When you’re deciding between the LL4148 and the 1N4148 diode, remember they’re similar but differ mainly in packaging. The LL4148 is an SMD diode in a SOD-80 package—great if you’re using surface-mount assembly—while the 1N4148 comes in a traditional DO-35 through-hole package, perfect if you’re hand-soldering or using a breadboard. Because of this, you can’t swap them directly on the same PCB.
Performance-wise, the 1N4148 can handle slightly higher voltage (100V vs. 75V) and current (200mA vs. 150mA), making it suitable if your circuit draws a bit more power. Both have the same switching speed and forward voltage drop, so if you switch packages, you’ll need to tweak your PCB layout accordingly.
Ll4148 for Logic Level Switching
If you’re working with high-speed digital circuits and logic-level switching, the LL4148 diode is a great pick. Why? Because it’s super fast, switching from on to off in just about 4 nanoseconds—perfect for reducing signal delays and distortions. It also has a low forward voltage drop (around 0.72V), meaning less power loss and stable signals. The LL4148 handles small currents (up to 150mA), making it ideal for logic-level circuits. Its compact SMD package (SOD-80) fits neatly into tight PCB spaces. Just remember: always check polarity, keep voltage and current within limits, and keep your PCB layout clean and short for best performance.
Ll4148 Smd Diode Application
If you’re designing circuits with high-speed digital signals, the LL4148 diode is a smart choice. Its super-fast switching speed (less than 4ns) makes it perfect for logic circuits, data communication, or oscillators. You can also use it for signal clamping or shaping, keeping voltage levels safe and protecting your chips. For ESD protection, placing it between your signal line and ground helps absorb static spikes, preventing damage. It’s excellent for relay coils or inductive loads, absorbing voltage spikes when the relay switches off. Just keep an eye on polarity (the cathode end is marked), stick to the rated voltage and current, and keep PCB traces short for best results.
Ll4148 Diode Recovery Time
If you’re working with fast-switching circuits, the LL4148 diode is ideal, thanks to its extremely short reverse recovery time—typically around 4 ns. But what does that really mean for you?
-
What’s reverse recovery time?
It’s basically how fast the diode can switch from conducting to blocking current. Shorter times mean cleaner signals and less distortion. -
Why does LL4148 stand out?
With its ultra-fast 4 ns recovery time, it’s perfect for high-speed digital circuits, logic gates, data communication, and precise switching applications. You get clearer signals and less energy loss. -
Things to remember:
Keep PCB wiring short to minimize interference. Also, avoid exceeding its 150 mA current rating, or you might damage it.
Ll4148 Fast Switching in Rf Circuits
If you’re dealing with RF circuits, the LL4148 diode is a great tool for quick switching, simple diode mixers, or protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes. It clamps excessive RF signals, preventing potential damage down the line, and its rapid response makes it excellent for accurately detecting and rectifying signals. Just remember that while LL4148 works smoothly at moderate RF frequencies (typically up to hundreds of MHz), it might struggle at GHz frequencies where specialized microwave diodes are more suitable. To get the best performance, always keep your PCB wiring short and clean to minimize parasitic effects like unwanted capacitance and inductance. Also, be careful with its maximum ratings—stick within 150 mA current and 75 V voltage limits to keep your diode running safely and reliably. By following these tips, you’ll ensure your RF circuits perform efficiently without unnecessary interference or damage.
Ll4148 in Arduino Protection Circuits

If you’re setting up an Arduino relay circuit with an NPN transistor, here’s what’s happening: When your Arduino’s GPIO pin outputs a HIGH signal, it activates the transistor through a base resistor, energizing the relay coil. This closes the relay contacts, turning your load on. When the GPIO goes LOW, the transistor turns off, the relay coil loses power, and the load switches off.
Now, here’s something important: you’ll notice two LL4148 diodes in the circuit. One diode placed across the relay coil absorbs voltage spikes when the relay switches off, protecting your transistor from damage. The other diode connected to the transistor’s base line protects your Arduino GPIO pin by clamping unexpected voltage spikes safely to the 5V line. This extra step prevents any harmful reverse voltage from hitting your Arduino, keeping everything safe and working smoothly.
Ll4148 Reverse Voltage Rating
When you’re using an LL4148 diode, keep in mind its maximum reverse voltage rating is 75 volts. In simpler terms, this means you should never apply more than 75 volts in reverse across the diode—otherwise, you’ll risk breaking it permanently. To play it safe, always ensure your circuit’s voltage spikes stay below this limit. If your setup tends to have sudden voltage surges or noisy conditions, it’s wise to either leave some extra voltage margin or choose a diode rated for higher voltages, like the 1N4448 or BAV103. This simple step helps you avoid unexpected failures and keeps your circuits reliable.






















