L9945 Hot Wheels & datasheet
Discover everything you need to know about the L9945 Hot Wheels with our comprehensive Reference Manual. This detailed guide provides all the specifications and technical details necessary to understand and utilize the L9945 to its fullest potential. Ideal for collectors and enthusiasts seeking in-depth information.
- MountingType: Surface Mount
- Applications: Automotive
- Current-Supply: -
- Package: 64-TQFP Exposed Pad

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
L9945
If you’re designing automotive electronics, the L9945 from STMicroelectronics is a smart choice. Think of it as a versatile power management chip perfect for driving various automotive loads, such as solenoids, relays, or small DC motors. Each of its multiple output channels can handle currents up to 1.3 A, making it powerful enough for most vehicle systems.
Safety and reliability are covered, too—it comes with built-in protections against short circuits, overcurrent, and overheating. There’s even an open-load detection feature to quickly identify wiring or load issues, simplifying troubleshooting.
Connecting this chip to your microcontroller is easy thanks to its SPI communication interface, allowing smooth integration into your system. Plus, it’s certified automotive-grade (AEC-Q100), meaning it’ll withstand harsh car environments and last longer.
Its flexible operating voltage range—from 5 to 28 volts—makes it suitable for nearly any automotive scenario. It’s truly an ideal component for modern vehicle control units.
L9945 Pinout

Here is the pin function diagram of L9945.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RESERVED | Reserved |
| 2 | DIS | External disable input |
| 3 | SCK | SPI clock input |
| 4 | SDI | SPI data input |
| 5 | NCS | SPI chip select |
| 6 | NRES | Reset input |
| 7 | GNDIO | Ground for digital I/O |
| 8 | SDO | SPI data output |
| 9 | VIO | Digital I/O supply voltage |
| 10 | NON8 | Output channel 8 control |
| 11 | NON7 | Output channel 7 control |
| 12 | NON6 | Output channel 6 control |
| 13 | NON5 | Output channel 5 control |
| 14 | NON4 | Output channel 4 control |
| 15 | NON3 | Output channel 3 control |
| 16 | NON2 | Output channel 2 control |
| 17 | NON1 | Output channel 1 control |
| 18 | VDD5 | 5V supply voltage |
| 19 | GND | Ground |
| 20 | GNDCP | Charge pump ground |
| 21 | VGBHI | Gate driver high voltage supply |
| 22 | CH4 | Charge pump capacitor connection |
| 23 | CH2 | Charge pump capacitor connection |
| 24 | CH3 | Charge pump capacitor connection |
| 25 | VPS | Battery voltage sense input |
| 26 | CH1 | Charge pump capacitor connection |
| 27 | NDIS | External disable input |
| 28 | EN6 | Enable input for channel 6 |
| 29 | SNGP5 | Source node gate pull-up for channel 5 |
| 30 | GNSP5 | Gate node source pull-down for channel 5 |
| 31 | DRN5 | Drain connection for channel 5 |
| 32 | GNSP6 | Gate node source pull-down for channel 6 |
| 33 | SNGP6 | Source node gate pull-up for channel 6 |
| 34 | BATT56 | Battery connection for channels 5 and 6 |
| 35 | DRN6 | Drain connection for channel 6 |
| 36 | PGND78 | Power ground for channels 7 and 8 |
| 37 | PGND56 | Power ground for channels 5 and 6 |
| 38 | SNGP7 | Source node gate pull-up for channel 7 |
| 39 | GNSP7 | Gate node source pull-down for channel 7 |
| 40 | DRN7 | Drain connection for channel 7 |
| 41 | GNSP8 | Gate node source pull-down for channel 8 |
| 42 | SNGP8 | Source node gate pull-up for channel 8 |
| 43 | BATT78 | Battery connection for channels 7 and 8 |
| 44 | DRN8 | Drain connection for channel 8 |
| Exposed Pad | GND | Ground (should be connected to PCB ground) |
Usage Notes and Precautions:
When you’re working with the L9945, there are a few things to keep in mind to make your design solid and reliable. First, always connect your power supply pins—like VDD5, VIO, and VPS—exactly as recommended in the datasheet. Proper grounding matters, too; tie all ground pins, especially the exposed thermal pad, to a solid ground plane to help with both performance and heat dissipation.
The SPI interface (pins SCK, SDI, SDO, and NCS) is how you’ll set up and diagnose your IC, so make sure these lines have good voltage stability and clean signals. Each output channel (OUT1 to OUT8) has unique control and power connections, and the datasheet gives clear details for different setups, including high-side, low-side, or H-bridge configurations.
Don’t overlook the safety pins—DIS and NDIS—which let you disable outputs for protection. And finally, solder the exposed pad directly to your PCB ground to handle heat efficiently.
L9945 Equivalent
Here is a comparison table of potential alternatives to the L9945 from STMicroelectronics:
| Feature | L9945 | L99DZ81EPTR | L9177ATR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | STMicroelectronics | STMicroelectronics | STMicroelectronics |
| Package | 64-TQFP with exposed pad | 64-TQFP | 64-TQFP with exposed pad |
| Channels | 8-channel MOSFET pre-driver | Multiple drivers for motors and loads | Multiple drivers for motors and loads |
| Output Configuration | High-side, low-side, H-Bridge, Peak & Hold | High-side, half-bridge, full-bridge | High-side, half-bridge, full-bridge |
| Operating Voltage | 3.8 V to 36 V (battery supply) | 5 V to 28 V | 6 V to 18 V |
| Logic I/O Voltage | 3.3 V / 5 V compatible | 5 V | 5 V |
| Diagnostics | Short to battery/ground, open-load | Short to battery/ground, open-load | Short to battery/ground, open-load |
| SPI Interface | Yes (32-bit) | Yes | Yes |
| Automotive Qualified | AEC-Q100 | AEC-Q100 | AEC-Q100 |
| Special Features | 64 programmable overcurrent thresholds, 10-bit ADC | Integrated charge pump, current monitor output | Programmable soft-start, current limitation |
| Typical Applications | Automotive ECUs, body electronics | Door actuator control, motor control | Engine management, motor control |
When you’re choosing an alternative device, don’t just pick based on specs alone—you’ve got to be sure it’ll fit seamlessly into your design. First off, make sure the substitute supports the exact output setups you need, like high-side, low-side, or H-bridge configurations, so you don’t run into compatibility headaches later.
Next, check the electrical details carefully. Confirm that the voltage range and current capabilities match your specific application requirements—getting this wrong could mean performance issues or even component damage.
Safety and diagnostics are also key. Look into whether the replacement chip offers similar protections, such as fault detection, overcurrent shutdown, and other diagnostics you’re relying on now.
SPI communication compatibility is critical, too—double-check the interface and protocols match your existing setup so you don’t have integration problems.
Finally, even if the package type is the same (like a 64-pin TQFP), always verify the pin arrangement. Minor differences could force you into unexpected PCB redesigns, so do your homework upfront to save yourself headaches later.
l9945ep Motor Driver
Typical Wiring Diagram for L9945EP Motor Driver IC
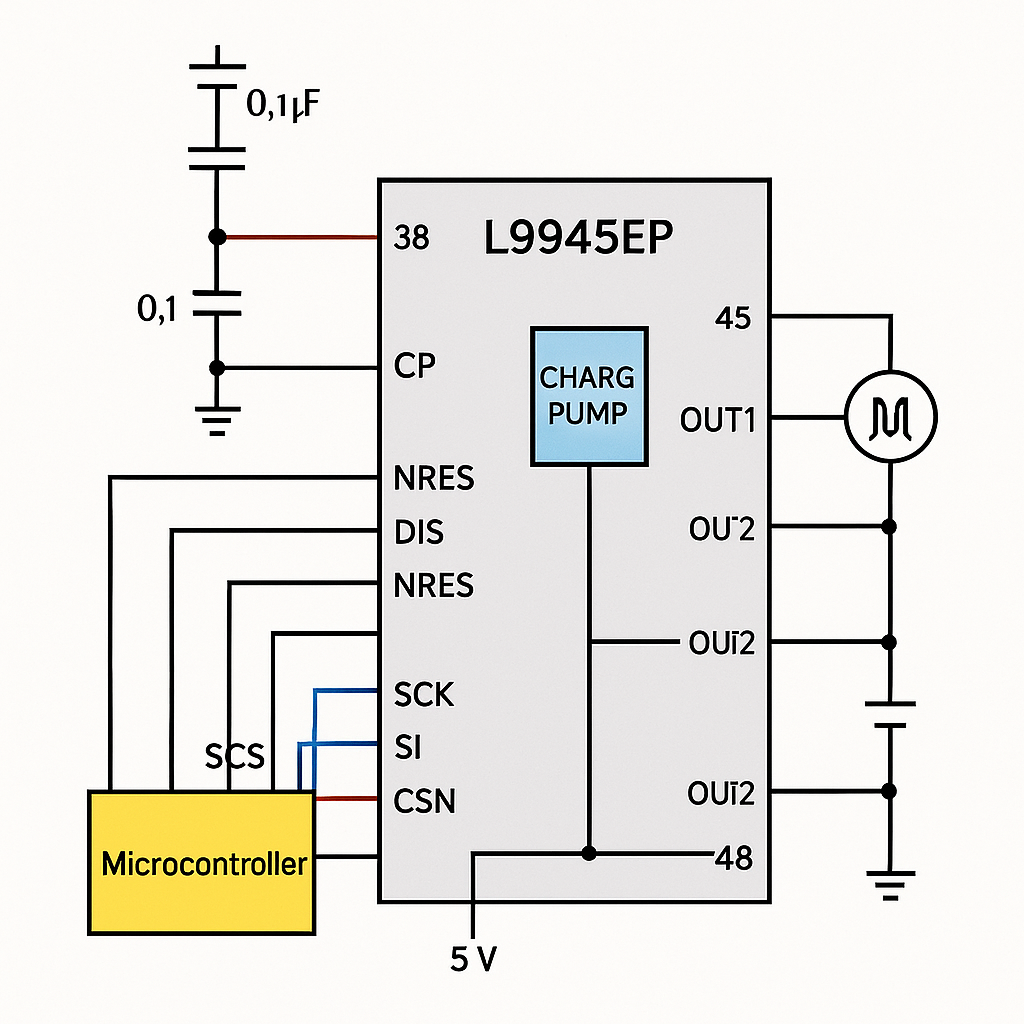
Here’s how it works in a practical sense: Your MCU first sets up the registers via the SPI bus. Then, whenever you want to activate a motor load, just pull the CSN line low and send your commands through the SI pin—like switching a certain channel output high or low. After that, the chip handles the rest automatically, driving your external motor load exactly as intended.
Inside the chip, a built-in charge pump combined with decoupling capacitors ensures there’s always enough gate voltage for smooth switching between the high-side and low-side switches. On top of that, the internal diagnostics continuously monitor the system’s status, so you can quickly catch and handle any issues, keeping your setup running safely and reliably.
l9945 vs l9958
Here’s a concise side-by-side comparison of the key parameters between L9945 and L9958, two automotive-grade motor driver ICs from STMicroelectronics:
| Parameter | L9945 | L9958 |
|---|---|---|
| Device Type | 8-channel MOSFET pre-driver | Integrated H-Bridge driver |
| Number of Channels | 8 configurable outputs | Single H-bridge output |
| Operating Voltage Range | 3.8 V to 36 V (battery supply) | 4.0 V to 28 V (battery supply) |
| Logic Supply Voltage | 4.5 V to 5.5 V | 4.5 V to 5.5 V |
| SPI Communication | Yes, 32-bit, daisy-chainable | Yes, 16-bit, daisy-chainable |
| Diagnostic Features | Short to battery, short to ground, open-load detection, 64 programmable overcurrent thresholds | Short to battery, short to ground, open-load detection, 4 programmable current thresholds (2.5 A to 8.6 A) |
| Integrated ADC | Yes, 10-bit ADC for voltage and temperature | No |
| Current Capability | Depends on external MOSFET selection | Integrated MOSFET up to 8.6 A (peak) |
| EMI Control | Programmable gate charge/discharge control | Integrated PWM slew rate control |
| Typical Application | General-purpose automotive control, configurable outputs, ECU systems | Dedicated DC motor and stepper motor applications |
When deciding between the L9945 and L9958 chips, it really comes down to what you’re trying to achieve. If you want flexibility—especially if your application involves various outputs or different load setups—the L9945 is probably your best bet. It works as a configurable MOSFET pre-driver, which means you’ll pair it with external MOSFETs. This setup lets you customize current capabilities and configurations exactly how you want them.
On the other hand, if you’re focused specifically on DC motors or stepper motors, you might prefer the L9958. It comes with MOSFETs already integrated, making your design simpler and more compact. However, this convenience does mean sacrificing a bit of flexibility in terms of current limits and configuration options.
Before swapping one chip for the other, carefully check your application’s current needs, integration requirements, and diagnostics. Also, watch out for differences in SPI interfaces (32-bit vs. 16-bit)—that’ll help you avoid integration headaches down the road.
l9945ep application notes & l9945 SPI motor driver
Relay and Solenoid Control
With the L9945EP, you can easily manage relays and solenoids by setting channels as either high-side or low-side drivers. This is perfect if you’re controlling things like fuel injectors, transmission solenoids, or valve actuators in cars. It’s a straightforward way to keep these components running smoothly and reliably.
H-Bridge Motor Control
If you’re controlling DC motors—like in power windows, seat adjusters, or mirrors—you can configure four channels of the L9945EP into an H-bridge. This lets you precisely control motor direction and speed, making it a great choice for all kinds of automotive positioning systems.
Peak and Hold Actuation
Another handy feature of the L9945EP is “peak and hold” control. Basically, it sends a high current initially (peak) to quickly activate a device, then switches to a lower current (hold) to maintain the device’s position. This approach is ideal for applications like fuel injectors because it provides rapid response and cuts down your overall power usage.
Power Window Control
If you’re designing a power window system, the L9945 SPI driver is a great choice. It precisely controls your window motors through an H-bridge setup. What’s nice about this driver is that it not only manages motor operation smoothly but also uses integrated diagnostics and an SPI interface to keep an eye on motor current. That means if something like a jam or overload occurs, you’ll get feedback right away, protecting your motors from unnecessary damage.
Seat Adjustment Systems
When it comes to seat adjustment systems in cars, the L9945 makes your job much easier. It smoothly manages the motors that adjust the seat position using PWM control. Plus, thanks to SPI-based communication, it ensures the seat moves exactly how you intend it to. This also helps you quickly diagnose any faults, improving the overall safety and comfort of the passengers.
The L9945EP is utilized in various automotive systems, including:
-
Engine Management: Controlling actuators and valves within the engine control unit (ECU).
-
Body Electronics: Managing functions like window lifters, seat adjusters, and lighting systems.
-
Chassis Systems: Operating components such as suspension controls and braking systems.
-
Safety Systems: Driving safety-critical loads with dedicated enable pins for enhanced control.
l9945ep evaluation board

The EVAL-L9945 is a handy evaluation board created by STMicroelectronics to help you easily test and prototype your designs using the L9945EP. This chip is an 8-channel MOSFET pre-driver that’s specifically designed for automotive use, and this board lets you check out all its features hands-on. You can set it up in different ways—whether you need a high-side, low-side, H-bridge, or peak & hold driving mode—so it’s really flexible for your various automotive projects.
More Like This
Also Add to Cart
Related Products
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.
Copyright © 2024 All Rights Reserved




.jpg)