BAT54C | Diode | Datasheet | Fairchild Yangzhou Yangjie Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd
- Brands: Yangzhou Yangjie Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd
- Download: BAT54C Datasheet PDF
- Price: inquiry
- In Stock: 12,704
- Voltage-DCReverse(Vr)(Max): 30 V
- Current-AverageRectified(Io)(perDiode): 200mA (DC)
- Voltage-Forward(Vf)(Max)@If: 1 V @ 100 mA
- Package: TO-236-3, SC-59, SOT-23-3

FREE delivery for orders over HK$250.00

Quick response, quick quotaton

Flash shipment,no worries after sales

Original channel,guarantee of the authentic products
Bat54c
If you’re looking at using the BAT54C diode, it’s a handy Schottky diode packaged neatly in a small SOT-23 form. With its common cathode design, it’s great for various circuits. It handles up to 30V reverse voltage and 200mA forward current easily. One key advantage you’ll appreciate is its low forward voltage drop—typically just 0.32V at 10mA—ideal for low-voltage scenarios. Plus, its extremely fast switching (less than 5ns recovery time) makes it perfect for high-frequency circuits. With minimal leakage current and a wide temperature range (-55°C to +125°C), it’s reliable in consumer electronics, battery protection, ESD circuits, and RF applications.
Bat54c Pinout
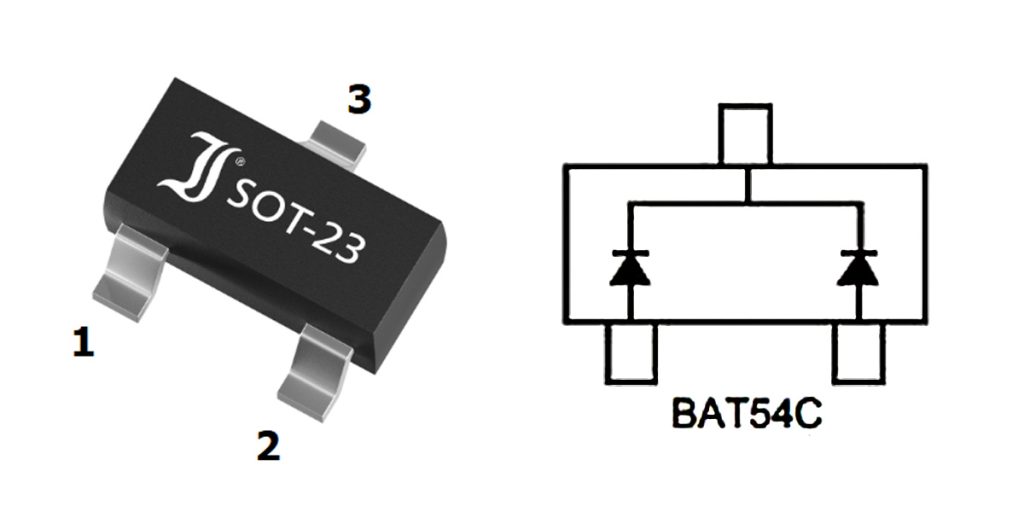
| Pin Number | Name | Function Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode 1 (A1) | Anode terminal of diode 1 |
| 2 | Anode 2 (A2) | Anode terminal of diode 2 |
| 3 | Cathode (K) | Common cathode terminal |
When you’re working with the BAT54C diode, remember it has a common cathode (pin 3), typically tied to ground or a low-voltage reference point. Pins 1 and 2 are the anodes, each usually protecting or rectifying separate signal or power lines. Be careful with the orientation on your PCB layout to avoid reversing connections, as that can disrupt your circuit’s function. For best performance, keep diode connections to your protected signals short to minimize noise and voltage drop. You’ll commonly use this diode configuration for tasks like signal protection, rectification, and ESD protection in various electronic designs.
Bat54c Equivalent Diode




| Parameter | BAT54C | BAS40-05 | BAT54S | BAS70-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Package Type | SOT-23 | SOT-23 | SOT-23 | SOT-23 |
| Configuration | Common Cathode (C) | Common Cathode (C) | Series (S) | Common Cathode (C) |
| Max Reverse Voltage (VR) | 30 V | 40 V | 30 V | 70 V |
| Max Forward Current (IF) | 200 mA | 120 mA | 200 mA | 70 mA |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF @10mA) | 0.32 V (typical) | 0.38 V (typical) | 0.32 V (typical) | 0.41 V (typical) |
| Reverse Recovery Time (trr) | <5 ns | <5 ns | <5 ns | <5 ns |
When you’re choosing a replacement diode for your BAT54C, first make sure the reverse voltage (VR) and maximum current (IF) ratings match or exceed the original specs for safety and reliability. Also, stick with common-cathode diodes like BAS40-05 or BAS70-05 to keep pin compatibility and avoid reworking your PCB layout. Avoid series configurations like the BAT54S, as they won’t directly swap in. If your circuit is sensitive to voltage drop, pick a diode with a similar or lower forward voltage (VF). Overall, BAS40-05 or BAS70-05 are great choices—they closely match your original BAT54C, ensuring your circuit continues running smoothly.
Bat54c Protection Circuit Example

Here’s how the BAT54C diode works in your DS3231 real-time clock circuit. It’s a common-cathode Schottky diode with two anodes, perfect for smoothly switching between your main 3.3V supply and a backup battery. When the main supply is active, it powers the RTC, keeping the battery idle and preserving its life. If your main supply drops out, the battery seamlessly takes over through the second diode, ensuring the clock keeps running. Thanks to its low voltage drop (around 0.3V), switching is efficient. Just keep the diode close to the RTC chip on your PCB for best performance.
Bat54c Diode Pair Application
The BAT54C diode pair is handy in a few practical applications you’ll often come across. For example, one common use is as an OR-ing diode for automatic power switching—like when a primary regulator drops out, it seamlessly switches over to battery backup, ensuring uninterrupted power. You’ll commonly find this setup powering real-time clocks, such as the DS3231.
Another great use is protecting sensitive pins and data lines from ESD (static discharges). Think of MCU GPIO pins or communication lines like USB, serial ports, or I²C buses—this diode pair prevents them from frying due to static shocks.
Lastly, it’s useful for clamping voltage spikes on high-speed signal lines, ensuring signals on interfaces like HDMI, USB high-speed data lines, or ADC inputs stay within safe limits and avoid damage.
Bat54c for Usb Esd Protection
The BAT54C diode pair is perfect if you’re looking to protect USB ports from static damage. It’s essentially two Schottky diodes sharing a common cathode, and it guards the USB data lines (D+ and D-) from ESD hits.
Under normal conditions, this diode stays off, letting your USB signals pass smoothly. But the moment there’s a sudden high-voltage spike—like when someone touches the USB port and static zaps it—the BAT54C instantly kicks in. It channels the excess voltage safely away, keeping your USB controller safe from harm.
One thing to keep in mind: place this diode as close as possible to the USB connector on your PCB. Shorter connections mean better protection. Also, always check you’re within its rated voltage and current limits to avoid unintended activation. For consumer gadgets or industrial gear, BAT54C is an affordable, compact solution that gets the job done.
Bat54c Low Forward Drop Diode
The BAT54C diode is great when designing circuits where every bit of power counts—especially in portable, battery-powered devices. What makes this diode stand out is its super low forward voltage, typically around 0.32 V at 10 mA. That’s way lower than the standard diode drop of about 0.7 V, meaning less wasted energy and longer battery life for your gadgets.
Another nice thing about the BAT54C is its ultra-fast switching capability—it responds in under 5 ns, perfect for high-frequency circuits. Plus, it has very low leakage current (under 2 µA), further reducing power drain when your circuit is idle.
When you’re using this diode, always make sure your current stays within its 200 mA limit and your voltage doesn’t exceed the 30 V rating. And don’t forget, keeping your PCB traces short and tidy will give you the best results.
Bat54c Schottky Diode Clamping
The BAT54C diode is your go-to choice if you’re looking to clamp voltage spikes and protect delicate electronics. Basically, it works by quickly turning on whenever your signal voltage goes beyond safe limits, either above the supply voltage (VCC) or below ground (GND). This instantly pulls the voltage back into a safe range, stopping your microcontrollers or other sensitive parts from getting damaged.
One thing you’ll like about the BAT54C is its low forward voltage—around 0.3 V—meaning less stress on your circuits. Plus, it switches super fast, responding almost instantly to any voltage spikes.
Just remember, use a suitable resistor (something like 100Ω to 1kΩ) to limit current through the diode, protecting it from burning out. Also, keep in mind it has a 30 V reverse voltage limit, so it’s ideal for low-voltage setups like microcontroller inputs, high-speed data lines, or precision circuits.
Bat54c Switching Speed Specs
The BAT54C diode is a great choice for any design needing quick switching, especially in high-frequency circuits. It switches incredibly fast—typically in around 5 nanoseconds or less—making it perfect for protecting high-speed signals or handling rapid voltage changes.
Another important thing to note is its low junction capacitance, typically about 10 pF. That’s pretty small, meaning it won’t distort your signals, even at higher frequencies. So, if you’re designing circuits for high-speed signal processing, fast rectification, or ESD protection, this diode fits perfectly.
When you use BAT54C, you’ll get reliable performance, as it reacts quickly to voltage spikes and prevents sensitive electronics from getting damaged. Just remember to stay within the recommended voltage and current limits, and you’ll have a reliable protection solution for your high-frequency applications.
.jpg)










;;2.jpg)