BSS84 | Datasheet | Circuit | Equivalent onsemi
- Tipo de FET: Canal P
- Voltaje de drenaje a fuente (Vdss): 50 voltios
- Drenaje continuo de corriente (Id) a 25 °C: 130mA (Ta)
- Paquete: Morir

Envío GRATUITO para pedidos superiores a HK$250.00

Respuesta rápida, cotización rápida.

Envío rápido, sin preocupaciones posventa.

Canal original, garantía de los productos auténticos.
BSS84-7-F cross reference MOSFET datasheet
Bss84
El BSS84 is an N-channel enhancement mode MOSFET, perfect for low-power switching applications. It’s commonly used in compact circuit designs, thanks to its small SOT-23 package.
Here’s what makes it stand out:
-
Tiene una maximum drain-source voltage (Vds) de -50V, handling reverse voltage up to 50V.
-
With a maximum drain current (Id) de -130mA, it’s great for circuits that need small current control.
-
El low gate threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) de aproximadamente -1.3V makes it ideal for low-voltage logic control.
-
Tiene una low Rds(on), meaning it operates with less heat and power loss.
You’ll find it in applications like low-power switches, digital circuits, y protección contra voltaje inverso. Its ability to switch quickly and perform efficiently makes it a great choice for battery-powered devices and other small electronics.
Bss84 Pinout
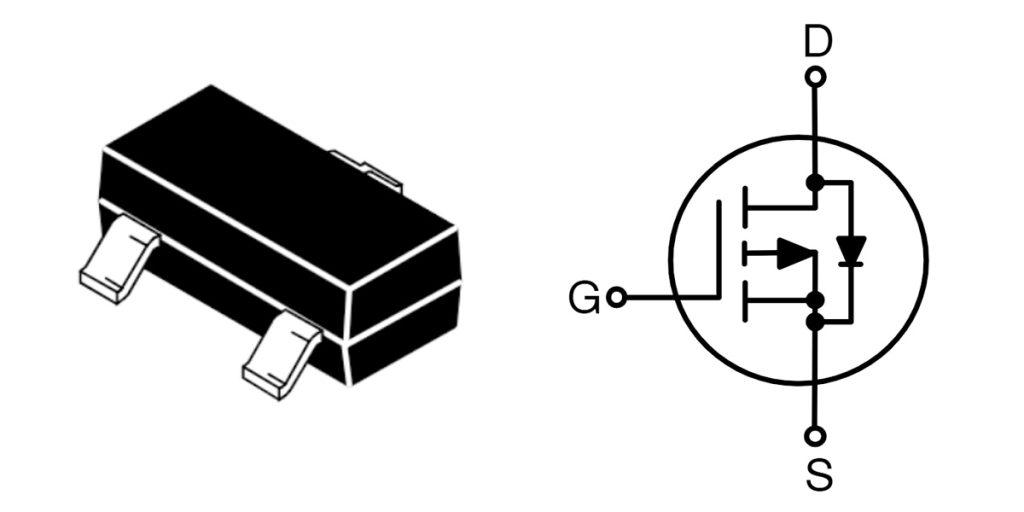
| Número PIN | Nombre del pin | Descripción de la función |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Puerta (G) | Control pin, controls the MOSFET’s switching state. |
| 2 | Fuente (S) | Source pin, current input. |
| 3 | Drenaje (D) | Drain pin, current output. |
Here are a few important things to keep in mind when using a MOSFET:
-
Gate-Source Voltage (Vgs): Always make sure the Vgs stays within the safe range, ideally under ±20V, to prevent damage.
-
On-Resistance (Rds(on)): As Vgs becomes more negative, Rds(on) decreases, so consider adjusting the voltage for optimal performance.
-
Temperature Effects: Higher temperatures can increase Rds(on), so take heat dissipation into account when designing your circuit.
-
Current Limits: Don’t exceed the maximum drain current rating, especially in high-temperature environments, to avoid damaging the MOSFET.
Bss84 Equivalent


| Parámetros | BSS84 | IRLML6402 |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 | SOT-23 |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V | -30V |
| Max Drain Current (Id) | -130mA | -100mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V ~ -3.0V | -1.5V ~ -3.0V |
| Rds(on) | 10Ω | 5Ω |
| Application Area | Switching, current limiting, voltage regulation | Low power switching, battery management |
When picking a replacement MOSFET, here are a few things to keep in mind:
-
Vgs(th) (Gate-Source Threshold Voltage): Choose a MOSFET with a similar Vgs(th) to the original for consistent switching performance.
-
Rds(on): To reduce power loss, go for a MOSFET with a low Rds(on) como el IRLML6402, which offers 5Ω. This is key for power efficiency.
Bss84 Load Switch Mosfet Circuit

This circuit shows an example of a BSS84 P-channel MOSFET used to control a DC motor. Here’s how it works:
-
El MOSFET acts as a switch to control current flow.
-
Vds = -10V: This shows the voltage difference between the MOSFET’s drain and source.
-
El control signal (Vo) changes the MOSFET’s state, turning the motor on or off.
-
R1 es un current-limiting resistor, protecting other components in the circuit.
When the control signal (Vo) is negative (like -5V), the MOSFET turns on and the motor runs. When the control signal is zero or positive, the MOSFET turns off, stopping the motor.
This setup is common in motor control systems y low-power switching applications.
Bss84 P Channel Mosfet for Low Side Switch
El BSS84 es un P-channel MOSFET and is typically used in high-side switching circuits. In a high-side switch, the source is connected to the positive power supply (Vcc), and the drain goes to the carga. The gate is controlled by an input signal, and the Vgs needs to be negative for the MOSFET to turn on.
For low-side switching, N-channel MOSFETs are a better choice. They are more efficient and easier to drive, as the source is connected to ground and only a positive gate voltage is needed to turn them on.
If you’re considering using the BSS84 for low-side switching, it’s not the best option since it requires a negative gate voltage. For better performance in low-side configurations, go for an MOSFET de canal N como el IRLZ44N.
Bss84 Arduino High-Side Control
To drive the BSS84 P-channel MOSFET with a 5V signal from an Arduino, you need an Transistor NPN como el 2N3904 for level shifting. Connect the collector of the transistor to the gate of the BSS84, the emitter to ground, and the base to the Arduino’s digital output through a 10kΩ resistor. When the Arduino outputs 5 V, the transistor turns on, pulling the gate low, which switches the MOSFET on and allows current through the load. When the Arduino outputs 0V, the transistor turns off, and the MOSFET switches off, stopping current to the load. This setup ensures proper control using the Arduino’s 5V logic.Bss84 Smd Package Specifications
| Parámetros | Values |
|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 (TO-236AB) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 2.90 mm x 1.60 mm x 1.15 mm |
| Lead Spacing | 0.95 mm |
| Peso | Approx. 0.02 g |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V |
| Max Continuous Drain Current (Id) | -130mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V to -3.0V |
| Drain-Source On Resistance (Rds(on)) | Typical 10Ω (Vgs = -5V) |
| Tipo de paquete | SMD (Surface Mount Device) |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount (SMT) |
| Polaridad | Canal P |
El BSS84 comes in a tiny SOT-23 package, making it perfect for tight spaces. It measures just 2.90mm x 1.60mm x 1.15mm, so it fits well into high-density, compact designs.
It’s a low-power P-channel MOSFET with a maximum drain current of -130mA, making it ideal for power management and low-power switching circuits. The SMD package allows for easy automated soldering, reducing production costs and improving efficiency.
Despite its small size, it offers great heat dissipation and is well-suited for modern electronics that need both compactness and efficient cooling. With a low Rds(on) de 10Ω, it ensures minimal power loss, making it perfect for low-current applications.
Bss84 for Reverse Polarity Protection
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET is a great choice for reverse polarity protection. Here’s how it works:
When the power is connected correctly, the source is linked to the positive voltage, and the drain goes to the load, with the gate grounded or set to the right voltage. The MOSFET conducts current, allowing the device to work normally.
The beauty of using a MOSFET como el BSS84 is its simplicity and efficiency—it automatically shuts off when the polarity is reversed, protecting your circuit. Plus, unlike relays, there’s no mechanical wear, making it more reliable and durable. It also uses low power and has a small SOT-23 package, perfect for tight spaces. Just make sure the Vds doesn’t exceed -50V, and the Identificación is below -130mA.
Bss84 Gate Voltage Threshold
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET has a gate-source threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) that determines when it turns on. For the BSS84, the Vgs(th) ranges from -1.0V to -3.0V. This means when the gate voltage is negative relative to the source voltage, the MOSFET starts conducting.
For instance, when the Vgs reaches -1.0V, the BSS84 starts to allow current through the source and drain. Keep in mind that Vgs(th) can change with temperature, so always ensure the gate voltage is sufficiently negative to properly turn the MOSFET on, especially in high-side switching applications.
BSS84-7-F cross reference MOSFET datasheet
Bss84
El BSS84 is an N-channel enhancement mode MOSFET, perfect for low-power switching applications. It’s commonly used in compact circuit designs, thanks to its small SOT-23 package.
Here’s what makes it stand out:
-
Tiene una maximum drain-source voltage (Vds) de -50V, handling reverse voltage up to 50V.
-
With a maximum drain current (Id) de -130mA, it’s great for circuits that need small current control.
-
El low gate threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) de aproximadamente -1.3V makes it ideal for low-voltage logic control.
-
Tiene una low Rds(on), meaning it operates with less heat and power loss.
You’ll find it in applications like low-power switches, digital circuits, y protección contra voltaje inverso. Its ability to switch quickly and perform efficiently makes it a great choice for battery-powered devices and other small electronics.
Bss84 Pinout

| Número PIN | Nombre del pin | Descripción de la función |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Puerta (G) | Control pin, controls the MOSFET’s switching state. |
| 2 | Fuente (S) | Source pin, current input. |
| 3 | Drenaje (D) | Drain pin, current output. |
Here are a few important things to keep in mind when using a MOSFET:
-
Gate-Source Voltage (Vgs): Always make sure the Vgs stays within the safe range, ideally under ±20V, to prevent damage.
-
On-Resistance (Rds(on)): As Vgs becomes more negative, Rds(on) decreases, so consider adjusting the voltage for optimal performance.
-
Temperature Effects: Higher temperatures can increase Rds(on), so take heat dissipation into account when designing your circuit.
-
Current Limits: Don’t exceed the maximum drain current rating, especially in high-temperature environments, to avoid damaging the MOSFET.
Bss84 Equivalent


| Parámetros | BSS84 | IRLML6402 |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 | SOT-23 |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V | -30V |
| Max Drain Current (Id) | -130mA | -100mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V ~ -3.0V | -1.5V ~ -3.0V |
| Rds(on) | 10Ω | 5Ω |
| Application Area | Switching, current limiting, voltage regulation | Low power switching, battery management |
When picking a replacement MOSFET, here are a few things to keep in mind:
-
Vgs(th) (Gate-Source Threshold Voltage): Choose a MOSFET with a similar Vgs(th) to the original for consistent switching performance.
-
Rds(on): To reduce power loss, go for a MOSFET with a low Rds(on) como el IRLML6402, which offers 5Ω. This is key for power efficiency.
Bss84 Load Switch Mosfet Circuit

This circuit shows an example of a BSS84 P-channel MOSFET used to control a DC motor. Here’s how it works:
-
El MOSFET acts as a switch to control current flow.
-
Vds = -10V: This shows the voltage difference between the MOSFET’s drain and source.
-
El control signal (Vo) changes the MOSFET’s state, turning the motor on or off.
-
R1 es un current-limiting resistor, protecting other components in the circuit.
When the control signal (Vo) is negative (like -5V), the MOSFET turns on and the motor runs. When the control signal is zero or positive, the MOSFET turns off, stopping the motor.
This setup is common in motor control systems y low-power switching applications.
Bss84 P Channel Mosfet for Low Side Switch
El BSS84 es un P-channel MOSFET and is typically used in high-side switching circuits. In a high-side switch, the source is connected to the positive power supply (Vcc), and the drain goes to the carga. The gate is controlled by an input signal, and the Vgs needs to be negative for the MOSFET to turn on.
For low-side switching, N-channel MOSFETs are a better choice. They are more efficient and easier to drive, as the source is connected to ground and only a positive gate voltage is needed to turn them on.
If you’re considering using the BSS84 for low-side switching, it’s not the best option since it requires a negative gate voltage. For better performance in low-side configurations, go for an MOSFET de canal N como el IRLZ44N.
Bss84 Arduino High-Side Control
To drive the BSS84 P-channel MOSFET with a 5V signal from an Arduino, you need an Transistor NPN como el 2N3904 for level shifting. Connect the collector of the transistor to the gate of the BSS84, the emitter to ground, and the base to the Arduino’s digital output through a 10kΩ resistor. When the Arduino outputs 5 V, the transistor turns on, pulling the gate low, which switches the MOSFET on and allows current through the load. When the Arduino outputs 0V, the transistor turns off, and the MOSFET switches off, stopping current to the load. This setup ensures proper control using the Arduino’s 5V logic.Bss84 Smd Package Specifications
| Parámetros | Values |
|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 (TO-236AB) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 2.90 mm x 1.60 mm x 1.15 mm |
| Lead Spacing | 0.95 mm |
| Peso | Approx. 0.02 g |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V |
| Max Continuous Drain Current (Id) | -130mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V to -3.0V |
| Drain-Source On Resistance (Rds(on)) | Typical 10Ω (Vgs = -5V) |
| Tipo de paquete | SMD (Surface Mount Device) |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount (SMT) |
| Polaridad | Canal P |
El BSS84 comes in a tiny SOT-23 package, making it perfect for tight spaces. It measures just 2.90mm x 1.60mm x 1.15mm, so it fits well into high-density, compact designs.
It’s a low-power P-channel MOSFET with a maximum drain current of -130mA, making it ideal for power management and low-power switching circuits. The SMD package allows for easy automated soldering, reducing production costs and improving efficiency.
Despite its small size, it offers great heat dissipation and is well-suited for modern electronics that need both compactness and efficient cooling. With a low Rds(on) de 10Ω, it ensures minimal power loss, making it perfect for low-current applications.
Bss84 for Reverse Polarity Protection
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET is a great choice for reverse polarity protection. Here’s how it works:
When the power is connected correctly, the source is linked to the positive voltage, and the drain goes to the load, with the gate grounded or set to the right voltage. The MOSFET conducts current, allowing the device to work normally.
The beauty of using a MOSFET como el BSS84 is its simplicity and efficiency—it automatically shuts off when the polarity is reversed, protecting your circuit. Plus, unlike relays, there’s no mechanical wear, making it more reliable and durable. It also uses low power and has a small SOT-23 package, perfect for tight spaces. Just make sure the Vds doesn’t exceed -50V, and the Identificación is below -130mA.
Bss84 Gate Voltage Threshold
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET has a gate-source threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) that determines when it turns on. For the BSS84, the Vgs(th) ranges from -1.0V to -3.0V. This means when the gate voltage is negative relative to the source voltage, the MOSFET starts conducting.
For instance, when the Vgs reaches -1.0V, the BSS84 starts to allow current through the source and drain. Keep in mind that Vgs(th) can change with temperature, so always ensure the gate voltage is sufficiently negative to properly turn the MOSFET on, especially in high-side switching applications.
BSS84-7-F cross reference MOSFET datasheet
Bss84
El BSS84 is an N-channel enhancement mode MOSFET, perfect for low-power switching applications. It’s commonly used in compact circuit designs, thanks to its small SOT-23 package.
Here’s what makes it stand out:
-
Tiene una maximum drain-source voltage (Vds) de -50V, handling reverse voltage up to 50V.
-
With a maximum drain current (Id) de -130mA, it’s great for circuits that need small current control.
-
El low gate threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) de aproximadamente -1.3V makes it ideal for low-voltage logic control.
-
Tiene una low Rds(on), meaning it operates with less heat and power loss.
You’ll find it in applications like low-power switches, digital circuits, y protección contra voltaje inverso. Its ability to switch quickly and perform efficiently makes it a great choice for battery-powered devices and other small electronics.
Bss84 Pinout

| Número PIN | Nombre del pin | Descripción de la función |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Puerta (G) | Control pin, controls the MOSFET’s switching state. |
| 2 | Fuente (S) | Source pin, current input. |
| 3 | Drenaje (D) | Drain pin, current output. |
Here are a few important things to keep in mind when using a MOSFET:
-
Gate-Source Voltage (Vgs): Always make sure the Vgs stays within the safe range, ideally under ±20V, to prevent damage.
-
On-Resistance (Rds(on)): As Vgs becomes more negative, Rds(on) decreases, so consider adjusting the voltage for optimal performance.
-
Temperature Effects: Higher temperatures can increase Rds(on), so take heat dissipation into account when designing your circuit.
-
Current Limits: Don’t exceed the maximum drain current rating, especially in high-temperature environments, to avoid damaging the MOSFET.
Bss84 Equivalent


| Parámetros | BSS84 | IRLML6402 |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 | SOT-23 |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V | -30V |
| Max Drain Current (Id) | -130mA | -100mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V ~ -3.0V | -1.5V ~ -3.0V |
| Rds(on) | 10Ω | 5Ω |
| Application Area | Switching, current limiting, voltage regulation | Low power switching, battery management |
When picking a replacement MOSFET, here are a few things to keep in mind:
-
Vgs(th) (Gate-Source Threshold Voltage): Choose a MOSFET with a similar Vgs(th) to the original for consistent switching performance.
-
Rds(on): To reduce power loss, go for a MOSFET with a low Rds(on) como el IRLML6402, which offers 5Ω. This is key for power efficiency.
Bss84 Load Switch Mosfet Circuit

This circuit shows an example of a BSS84 P-channel MOSFET used to control a DC motor. Here’s how it works:
-
El MOSFET acts as a switch to control current flow.
-
Vds = -10V: This shows the voltage difference between the MOSFET’s drain and source.
-
El control signal (Vo) changes the MOSFET’s state, turning the motor on or off.
-
R1 es un current-limiting resistor, protecting other components in the circuit.
When the control signal (Vo) is negative (like -5V), the MOSFET turns on and the motor runs. When the control signal is zero or positive, the MOSFET turns off, stopping the motor.
This setup is common in motor control systems y low-power switching applications.
Bss84 P Channel Mosfet for Low Side Switch
El BSS84 es un P-channel MOSFET and is typically used in high-side switching circuits. In a high-side switch, the source is connected to the positive power supply (Vcc), and the drain goes to the carga. The gate is controlled by an input signal, and the Vgs needs to be negative for the MOSFET to turn on.
For low-side switching, N-channel MOSFETs are a better choice. They are more efficient and easier to drive, as the source is connected to ground and only a positive gate voltage is needed to turn them on.
If you’re considering using the BSS84 for low-side switching, it’s not the best option since it requires a negative gate voltage. For better performance in low-side configurations, go for an MOSFET de canal N como el IRLZ44N.
Bss84 Arduino High-Side Control
To drive the BSS84 P-channel MOSFET with a 5V signal from an Arduino, you need an Transistor NPN como el 2N3904 for level shifting. Connect the collector of the transistor to the gate of the BSS84, the emitter to ground, and the base to the Arduino’s digital output through a 10kΩ resistor. When the Arduino outputs 5 V, the transistor turns on, pulling the gate low, which switches the MOSFET on and allows current through the load. When the Arduino outputs 0V, the transistor turns off, and the MOSFET switches off, stopping current to the load. This setup ensures proper control using the Arduino’s 5V logic.Bss84 Smd Package Specifications
| Parámetros | Values |
|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 (TO-236AB) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 2.90 mm x 1.60 mm x 1.15 mm |
| Lead Spacing | 0.95 mm |
| Peso | Approx. 0.02 g |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V |
| Max Continuous Drain Current (Id) | -130mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V to -3.0V |
| Drain-Source On Resistance (Rds(on)) | Typical 10Ω (Vgs = -5V) |
| Tipo de paquete | SMD (Surface Mount Device) |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount (SMT) |
| Polaridad | Canal P |
El BSS84 comes in a tiny SOT-23 package, making it perfect for tight spaces. It measures just 2.90mm x 1.60mm x 1.15mm, so it fits well into high-density, compact designs.
It’s a low-power P-channel MOSFET with a maximum drain current of -130mA, making it ideal for power management and low-power switching circuits. The SMD package allows for easy automated soldering, reducing production costs and improving efficiency.
Despite its small size, it offers great heat dissipation and is well-suited for modern electronics that need both compactness and efficient cooling. With a low Rds(on) de 10Ω, it ensures minimal power loss, making it perfect for low-current applications.
Bss84 for Reverse Polarity Protection
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET is a great choice for reverse polarity protection. Here’s how it works:
When the power is connected correctly, the source is linked to the positive voltage, and the drain goes to the load, with the gate grounded or set to the right voltage. The MOSFET conducts current, allowing the device to work normally.
The beauty of using a MOSFET como el BSS84 is its simplicity and efficiency—it automatically shuts off when the polarity is reversed, protecting your circuit. Plus, unlike relays, there’s no mechanical wear, making it more reliable and durable. It also uses low power and has a small SOT-23 package, perfect for tight spaces. Just make sure the Vds doesn’t exceed -50V, and the Identificación is below -130mA.
Bss84 Gate Voltage Threshold
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET has a gate-source threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) that determines when it turns on. For the BSS84, the Vgs(th) ranges from -1.0V to -3.0V. This means when the gate voltage is negative relative to the source voltage, the MOSFET starts conducting.
For instance, when the Vgs reaches -1.0V, the BSS84 starts to allow current through the source and drain. Keep in mind that Vgs(th) can change with temperature, so always ensure the gate voltage is sufficiently negative to properly turn the MOSFET on, especially in high-side switching applications.
BSS84-7-F cross reference MOSFET datasheet
Bss84
El BSS84 is an N-channel enhancement mode MOSFET, perfect for low-power switching applications. It’s commonly used in compact circuit designs, thanks to its small SOT-23 package.
Here’s what makes it stand out:
-
Tiene una maximum drain-source voltage (Vds) de -50V, handling reverse voltage up to 50V.
-
With a maximum drain current (Id) de -130mA, it’s great for circuits that need small current control.
-
El low gate threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) de aproximadamente -1.3V makes it ideal for low-voltage logic control.
-
Tiene una low Rds(on), meaning it operates with less heat and power loss.
You’ll find it in applications like low-power switches, digital circuits, y protección contra voltaje inverso. Its ability to switch quickly and perform efficiently makes it a great choice for battery-powered devices and other small electronics.
Bss84 Pinout

| Número PIN | Nombre del pin | Descripción de la función |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Puerta (G) | Control pin, controls the MOSFET’s switching state. |
| 2 | Fuente (S) | Source pin, current input. |
| 3 | Drenaje (D) | Drain pin, current output. |
Here are a few important things to keep in mind when using a MOSFET:
-
Gate-Source Voltage (Vgs): Always make sure the Vgs stays within the safe range, ideally under ±20V, to prevent damage.
-
On-Resistance (Rds(on)): As Vgs becomes more negative, Rds(on) decreases, so consider adjusting the voltage for optimal performance.
-
Temperature Effects: Higher temperatures can increase Rds(on), so take heat dissipation into account when designing your circuit.
-
Current Limits: Don’t exceed the maximum drain current rating, especially in high-temperature environments, to avoid damaging the MOSFET.
Bss84 Equivalent


| Parámetros | BSS84 | IRLML6402 |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 | SOT-23 |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V | -30V |
| Max Drain Current (Id) | -130mA | -100mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V ~ -3.0V | -1.5V ~ -3.0V |
| Rds(on) | 10Ω | 5Ω |
| Application Area | Switching, current limiting, voltage regulation | Low power switching, battery management |
When picking a replacement MOSFET, here are a few things to keep in mind:
-
Vgs(th) (Gate-Source Threshold Voltage): Choose a MOSFET with a similar Vgs(th) to the original for consistent switching performance.
-
Rds(on): To reduce power loss, go for a MOSFET with a low Rds(on) como el IRLML6402, which offers 5Ω. This is key for power efficiency.
Bss84 Load Switch Mosfet Circuit

This circuit shows an example of a BSS84 P-channel MOSFET used to control a DC motor. Here’s how it works:
-
El MOSFET acts as a switch to control current flow.
-
Vds = -10V: This shows the voltage difference between the MOSFET’s drain and source.
-
El control signal (Vo) changes the MOSFET’s state, turning the motor on or off.
-
R1 es un current-limiting resistor, protecting other components in the circuit.
When the control signal (Vo) is negative (like -5V), the MOSFET turns on and the motor runs. When the control signal is zero or positive, the MOSFET turns off, stopping the motor.
This setup is common in motor control systems y low-power switching applications.
Bss84 P Channel Mosfet for Low Side Switch
El BSS84 es un P-channel MOSFET and is typically used in high-side switching circuits. In a high-side switch, the source is connected to the positive power supply (Vcc), and the drain goes to the carga. The gate is controlled by an input signal, and the Vgs needs to be negative for the MOSFET to turn on.
For low-side switching, N-channel MOSFETs are a better choice. They are more efficient and easier to drive, as the source is connected to ground and only a positive gate voltage is needed to turn them on.
If you’re considering using the BSS84 for low-side switching, it’s not the best option since it requires a negative gate voltage. For better performance in low-side configurations, go for an MOSFET de canal N como el IRLZ44N.
Bss84 Arduino High-Side Control
To drive the BSS84 P-channel MOSFET with a 5V signal from an Arduino, you need an Transistor NPN como el 2N3904 for level shifting. Connect the collector of the transistor to the gate of the BSS84, the emitter to ground, and the base to the Arduino’s digital output through a 10kΩ resistor. When the Arduino outputs 5 V, the transistor turns on, pulling the gate low, which switches the MOSFET on and allows current through the load. When the Arduino outputs 0V, the transistor turns off, and the MOSFET switches off, stopping current to the load. This setup ensures proper control using the Arduino’s 5V logic.Bss84 Smd Package Specifications
| Parámetros | Values |
|---|---|
| Tipo de paquete | SOT-23 (TO-236AB) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 2.90 mm x 1.60 mm x 1.15 mm |
| Lead Spacing | 0.95 mm |
| Peso | Approx. 0.02 g |
| Max Reverse Voltage (Vds) | -50V |
| Max Continuous Drain Current (Id) | -130mA |
| Gate-Source Threshold Voltage (Vgs(th)) | -1.0V to -3.0V |
| Drain-Source On Resistance (Rds(on)) | Typical 10Ω (Vgs = -5V) |
| Tipo de paquete | SMD (Surface Mount Device) |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount (SMT) |
| Polaridad | Canal P |
El BSS84 comes in a tiny SOT-23 package, making it perfect for tight spaces. It measures just 2.90mm x 1.60mm x 1.15mm, so it fits well into high-density, compact designs.
It’s a low-power P-channel MOSFET with a maximum drain current of -130mA, making it ideal for power management and low-power switching circuits. The SMD package allows for easy automated soldering, reducing production costs and improving efficiency.
Despite its small size, it offers great heat dissipation and is well-suited for modern electronics that need both compactness and efficient cooling. With a low Rds(on) de 10Ω, it ensures minimal power loss, making it perfect for low-current applications.
Bss84 for Reverse Polarity Protection
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET is a great choice for reverse polarity protection. Here’s how it works:
When the power is connected correctly, the source is linked to the positive voltage, and the drain goes to the load, with the gate grounded or set to the right voltage. The MOSFET conducts current, allowing the device to work normally.
The beauty of using a MOSFET como el BSS84 is its simplicity and efficiency—it automatically shuts off when the polarity is reversed, protecting your circuit. Plus, unlike relays, there’s no mechanical wear, making it more reliable and durable. It also uses low power and has a small SOT-23 package, perfect for tight spaces. Just make sure the Vds doesn’t exceed -50V, and the Identificación is below -130mA.
Bss84 Gate Voltage Threshold
El BSS84 P-channel MOSFET has a gate-source threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) that determines when it turns on. For the BSS84, the Vgs(th) ranges from -1.0V to -3.0V. This means when the gate voltage is negative relative to the source voltage, the MOSFET starts conducting.
For instance, when the Vgs reaches -1.0V, the BSS84 starts to allow current through the source and drain. Keep in mind that Vgs(th) can change with temperature, so always ensure the gate voltage is sufficiently negative to properly turn the MOSFET on, especially in high-side switching applications.
Más como esto
IRFU9024NPBF
Rectificador internacional
FDG6335N
onsemi
MMBFJ201
onsemi
IRF3205PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP1405PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRF3205ZSTRLPBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP4229PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFB7437PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRLR9343TRPBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP4468PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRF640NSTRLPBF
Rectificador internacional
FDS6375
Semiconductor nacional
Añadir también al carrito
DMP3028LFDE-7
Diodos incorporados
FDN306P
onsemi
STF10LN80K5
STMicroelectrónica
FDPF18N50
onsemi
DMN2300UFB4-7B
Diodos incorporados
STB15N80K5
STMicroelectrónica
TP0610K-T1-E3
Vishay Siliconix
STW36N60M6
STMicroelectrónica
IRF9530NPBF
Tecnologías Infineon
IPT60R028G7XTMA1
Tecnologías Infineon
AUIRFR4620TRL
Rectificador internacional
AO3407
Alfa y Omega Semiconductor Inc.
Productos relacionados
IRFU9024NPBF
Rectificador internacional
FDG6335N
onsemi
MMBFJ201
onsemi
IRF3205PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP1405PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRF3205ZSTRLPBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP4229PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFB7437PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRLR9343TRPBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP4468PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRF640NSTRLPBF
Rectificador internacional
FDS6375
Semiconductor nacional
IRFB4332PBF
Rectificador internacional
IRFP3306PBF
Rectificador internacional
NVTFS5811NLTAG
onsemi
NVTFS4823NTWG
onsemi
NVD5117PLT4G
onsemi
IRF200S234
Tecnologías Infineon
IRF840PBF
Tecnologías Infineon
AO4407
Alfa y Omega Semiconductor Inc.
2SK3377-Z-E1-AZ
Renesas Electronics America Inc
NVD5867NLT4G
onsemi
NVMFS5A160PLZWFT1G
onsemi
FDWS9510L-F085
onsemi
FDWS9509L-F085
onsemi
NVTFS5826NLWFTAG
onsemi
AON7401L
Alfa y Omega Semiconductor Inc.
AO4407AL
Alfa y Omega Semiconductor Inc.
AO3407
Alfa y Omega Semiconductor Inc.
CPH3461-TL-W
onsemi

~~3.jpg)




.jpg)









.jpg)