Everything About MCBs( Miniature Circuit Breaker): Why You Need It
Author:admin Date: 2025-04-02 07:16 Views:132

Whether in a home or office setup, sensitive electronics are in place. The worst that can happen is if they are exposed to overcurrent due to an overload or short circuit. Sometimes, this could damage the devices. Devices such as an MCB (miniature circuit breaker) are needed to protect them.
Are you interested in protecting your electronics from overcurrents? Learn more about MCBs and how they can save you a lot.
What is an MCB?
An MCB or miniature circuit breaker is an electrical switch that protects circuits from overcurrents. When a circuit shorts or overloads, the MCB automatically trips and interrupts the flow of electricity to protect the equipment or electronics.
This protection capability makes the electrical MCB an important part of your home, office, or industry electrical setup. The market offers several options that vary based on application and ability.
How Does an MCB Work?
Whether it is an AC or DC MCB circuit breaker, the operation is usually the same. When overcurrent happens which means the current is more than the rated MCB capacity, a bimetallic strip in it heats and bends.
When the strip bends, it releases a latch that opens the contacts in the MCB, interrupting the current flow. The result is preventing further damage to the appliances or circuit.
Another way the MCB works is when there is a short circuit. In this case, a sudden surge of current flows through a magnetic coil, resulting in a strong magnetic field that pulls the trip lever. At this point, the contacts are opened, interrupting the current flow.
Once the MCB trips, there is the choice of resetting it manually or automatically depending on the type.
You simply flip the switch back to the “ON” status to reconnect power to the circuit. Keep in mind the MCB will trip again if you do not correct the fault. So, ensure the fault is correct first and then return the MCB to the ON status.
Types of MCBs
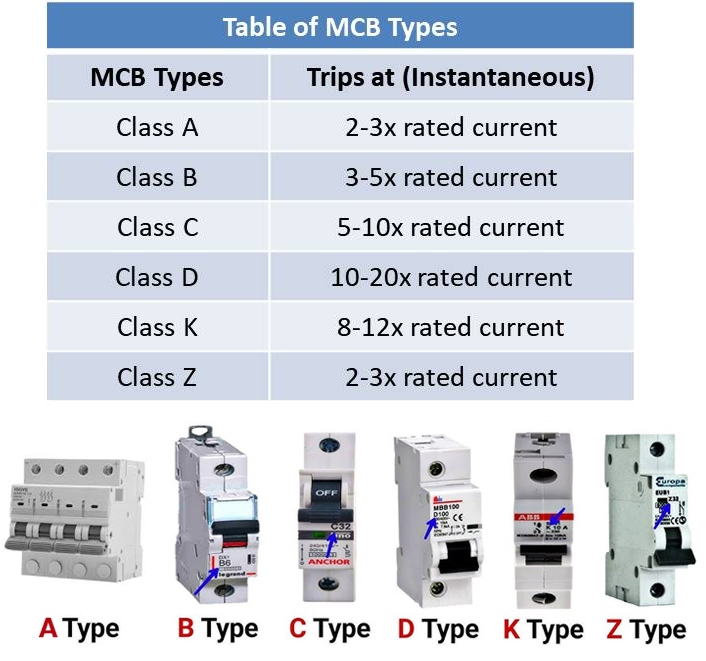
You will come across many types of MCBs in the market. They are designed to work based on the applications. As such, you would get some being more sensitive than others because of the application.
The popular types in the market include types A, B, C, D, K, and Z.
Type A are the most sensitive MCBs available. They are built for extremely sensitive electronics, medical devices, and control circuits, which require fast tripping to avoid damage.
Type B MCBs are commonly used in residential properties since current surges are less common, but they provide protection in case one happens. They can still be used in industrial units, depending on the need. These MCBs will trip if the power is five times the rated limit.
Type C MCBs are designed to trip if the current is 10 times the rated capacity. These are usually used in applications that consume a lot of power. Expect to come across them in industrial or commercial applications. The Type C MCB has more protection capacity than Type B, so you might find them being used in Type B applications sometimes.
Type D MCBs are the least sensitive. They have a surge capacity of 10 to 20 times their rated power capacity. These MCBs work great for devices such as X-ray machines, motors, and other devices needing more power.
Type K and Z are not very common, but have specific applications. For example, Type K is for applications with high harmonics. Type Z works well for very sensitive equipment.
Applications of MCBs
Residential Applications
As expected, an MCB will be vital for protecting your household appliances, lighting, and other equipment from potential damage due to short circuits and overloads. The automatic disconnection of power is vital for additional protection against fire and electrical shock.
Commercial Applications
You can find so many sensitive electronics in a commercial setup. That is why you need the MCB to protect them against the surge in power. Such include office equipment, lighting systems, and HVAC units. The same goes for the commercial refrigerators and industrial ovens.
Industrial Applications
You can get a 1000A MCB in an industry vital for protecting industrial equipment. We are talking of equipment such as pumps, machinery, and others that may be damaged due to short circuits or overcurrent.
To ensure the best protection, MCBs are often used in conjunction with other devices such as fuses, relays, and contractors.
Automotive Applications
MCBs can also be found in vehicles. Their job is to ensure that the various components, such as wipers, lights, and motors, are always protected from short-circuit scenarios.
You should always expect the best protection when you use MCB in a circuit. Make sure you choose the best one from top brands.
How to Choose an MCB
Before choosing a 200 amp MCB panel or 3-phase MCB busbar, it is vital to get a few things right. Below, we guide you in selecting the best MCB for your application.
Calculate the Total Load Current
The MCB will only work correctly for your circuit if adequately sized. By sizing, we mean that it should be able to support the total current needs of the devices in the circuit.
Start by adding up the power ratings of the devices and convert that to amps to get the current. This is done by dividing the total power by the voltage of the electricity supply.
Once you get the current load, apply a safety margin to account for possible surges so that the MCB can handle occasional overloads.
Buy the Right MCB Type
There are different types of MCBs in the market, each with a specific application. For example, Type B MCBs are meant for general residential use. This is because surges in residential areas are not common.
If you need to handle heavy industrial applications, we recommend Type D and Type K MCBs. For sensitive electronic circuits, Type A and Type Z will do a good job.
Breaking Capacity
The breaking capacity is what the MCB can safely interrupt. This figure is usually given as kiloamperes or kA. As an example, a 10kA MCB will safely interrupt current of up to 10,000 amperes.
The capacity should be more than the load current. Once you have calculated the load current, it should be possible to choose an MCB that can handle the circuit needs and still protect it.
MCB Pole Types
The poles, in this case, indicate the number of live wires that can be connected to the MCB. So, you can get 1-pole, 2-pole, and more.
A 1-pole MCB is common for residential settings where a single live wire should do the job. You would get the 2-pole and 3-pole MCBs in commercial and industrial settings where two or more live wires might be needed to run the machines.
MCB Voltage Rating
Just as the current rating is important, the voltage rating is also critical. For example, residential power supply would be either 240 volts or 415 volts. You should be able to find the voltage rating on the MCB itself so that you choose accordingly. Make sure that the voltage rating is equal to or more than the circuit’s nominal voltage.
How to Install an MCB
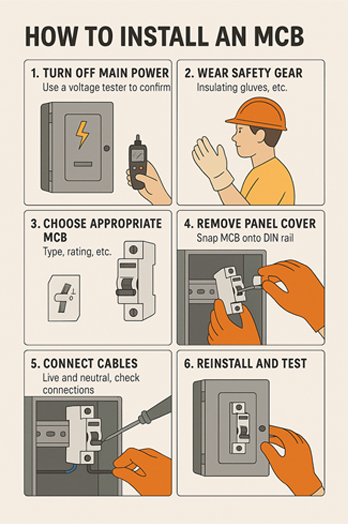
Before you can start installing the MCB, take precautions. First, turn off the main power and use a voltage tester to confirm there is no power in the circuit. Make sure to also wear safety gear, such as insulating gloves, for protection against electric shock.
At this point, you should have chosen the right MCB for the application. This is based on MCB type, its rating, and other features. Follow these steps to install the MCB.
- Remove the cover of the switchboard panel.
- Insert the MCB into the desired location. This is usually on a DIN rail, and press it so that it clicks into position.
- Connect the live and neutral wires as per the connection points. Check if all connections are secure.
- Use a voltage tester to see if the MCB is providing the protection as it should.
- Install the switchboard panel back into its position. Turn on the MCB to check it is working.
How to Maintain MCBs
There are a few things you can do to help keep the MCBs in good condition. Here are some maintenance tips to consider.
- Try to keep the MCB clean and check for visible damage or defects. Sometimes, the MCBs are kept in harsh environments, so keeping them clean should help ensure the MCB works excellently.
- Look for signs of corrosion on the metal parts of the MCB. Damp conditions or moisture can potentially damage the various parts of the MCB. Keeping the metal contacts free from rust or corrosion will improve the conductivity.
- If you notice there are wires protruding out of the MCB, make sure that you have them rewired. Having hanging wires can potentially lead to electrocution.
- We also recommend testing the mechanical operations of the MCB switch. The good thing about MCBs is that they are tested at the factory, but you can test them as well to see if they can keep working as expected. The MCB switch should perform at least five cycles of on and off operations without jamming or slipping.
- As for performance testing, there are a couple of tests that can be done. Examples include delay testing and instantaneous testing. Delay testing for checking to see if the tripping time of the MCB is correct in case it is overloaded. As for the instantaneous MCB testing, the technician will check if the tripping is done within the expected timeframe to ensure the safety of the equipment.
MCBs vs. Fuse vs. RCCB vs. MCCB
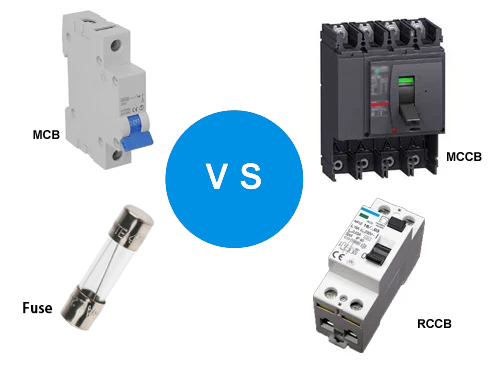
There are a number of safety devices you can expect in a circuit. Other than the MCB, the others include MCCB, RCCB, and fuses.
You might wonder, what is the difference between the MCB and MCCB? The MCCB or molded case circuit breaker works just like the MCB. The only difference is that it is meant for higher current ratings and more complicated circuits. You can expect to find it in large industrial installations where high current protection is necessary.
The RCCB, or residual current circuit breaker, helps protect against electric shock by detecting and interrupting the flow of leakage current. Leakage current is the type of current flowing through an unintended path, such as a person.
The RCCB monitors if the current flows in the neutral and live wires. If there is an imbalance, the MCB will trip the circuit. It is an essential add-on for homes or workplaces where there is a high risk of electric shock. Examples include bathrooms and outdoor areas.
What about the difference between MCB and fuse? The fuse is also vital for protecting against overloads and short circuits just as an MCB. The difference is that a wire melts and breaks the circuit in fuses to prevent current flow. So, to turn on the circuit, you have to replace the fuse with a new one, unlike the MCB, where you only have to switch it on.
Conclusion
An electric MCB panel remains an important part of your residential or commercial circuit. Expect it to be the best protection for your equipment, as it ensures the devices and equipment are safe from overcurrent and short-circuiting. It is key to always choose the right type of MCB for your needs. If you need sensitive MCBs, type A will be the right one, and for residential use, get the type B MCBs. Get yourself an MCB from a top brand to ensure the quality and performance are the best.


