An Essential Guide to Fuses: Types, How They Work, and Applications
Author:signbobo Date: 2025-04-17 09:36 Views:96
Circuit protection remains an important aspect of electronic devices. You may come across circuit breakers as the common way of protecting your device from surges. However, there are many other options as well. That is where fuses come in to also help with circuit protection.

what is a fuse?
A fuses is an electrical safety device vital for protecting the circuits from damage as they interrupt current flow if it exceeds a given threshold. A fuse is built with a thin metal wire that melts and breaks if the current is more than the expected rating. This usually happens during an overload or short circuit situation.

Ferrule Fuse
If the overload current is cut short, it does not reach the appliances or other sensitive electronics in the circuit. This prevents damage to the appliance, which can save you a lot in terms of replacing it.
Why Use Fuses?
Whether you are looking for car fuses or those for appliances, they all serve the same role. The first one is overload protection. The work of the fuse is to protect the circuits from drawing too much current. If a circuit is exposed to too much current, it leads to overheating and potentially damaging the appliances. Sometimes it can lead to fires.
Short circuit protection is also important. The fuse blows when current flows through an unintended path, interrupting the electricity flow. This is key in preventing harm to the appliance.
Of course, safety is also a reason to get fuses. Compared to circuit breakers, fuses remain an easy and inexpensive method for protecting circuits.
How fast are the fuses? Expect that fuses will still be fast in breaking the circuit if there is an overload or short circuit. This is key in ensuring faster protection for your circuit.
How Do Fuses Work
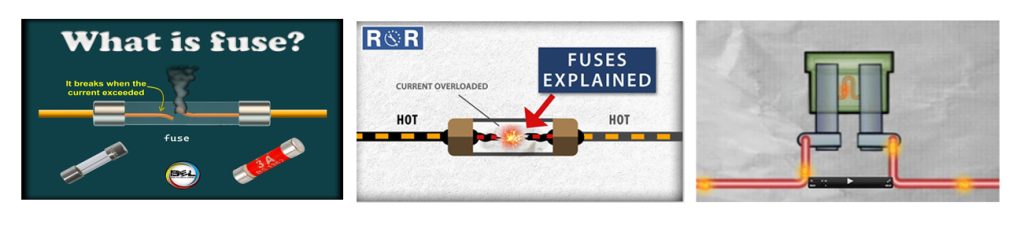
Regardless of the application, the working principle is the same. A fuse is built to break the flow of current when the current exceeds a certain limit. This is based on the fuse rating. That is why you will come across different types of fuse ratings, such as 30amp or 40-amp fuse.
At the center of the whole operation is a thin metal wire in a fuse. The metal wire connects to the ends of the fuse. So, if there is a normal range of current passing through the wire, there should be no problem, as it will conduct and power the appliance.
However, if there is an excessive amount of current flowing in the thin wire, it will melt and break the continuity. A fuse heats and melts quite fast that the current will not cause damage to the connected appliance.
Types of Fuses
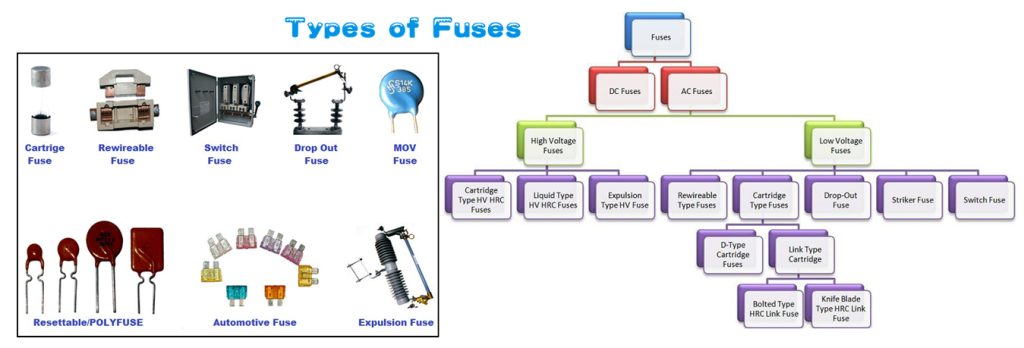
Automotive fuses are not the only options in the market. You will be surprised to find so many other uses available, each with a different purpose. Let us look at them below.
Based on the Current Type
- AC fuses – they are designed to work with alternating current. You will come across them in industrial settings as well as household appliances.
- DC fuses – if you need something for your vehicle, then get a DC fuse. These fuses are built to work with direct current circuits.
Based on Application
- High voltage fuses – this fuse type works well for high voltage levels. For this reason, it is common in industrial power systems.
- Low voltage fuses – these are common commercial and residential settings to protect circuits.
- Cartridge fuses – they come with a cylindrical body and hence the name. They offer reliability and protection for industrial equipment and appliances as well.
- Blade fuses – the design gives them the name blade. These are common in cars and some other devices. They are good for their compact nature and are easy to replace.
- High rupturing capacity fuses or HRC fuses – these fuses can interrupt high fault currents. As such, they are common in industrial settings.
- Thermal fuses – these fuses protect devices from overheating. They simply melt when exposed to very high temperatures.
- Resettable fuses – yes, there are resettable fuses. In this case, you can reset them after tripping. This is unlike other types of fuses that need replacement.
- Time-delay fuses—This design delays tripping under normal overloads to ensure there are no unnecessary circuit interruptions.
You will encounter more types of fuses depending on the application. It all depends on how they are built and where they will be used.
Understanding Fuse Sizes
Fuse sizes are measured in terms of amps (A). This determines the maximum current that can go through the fuse before it melts and breaks the circuit. Having the right fuse size important to ensure the appliances connected to the circuit as well protected.
Having a larger rating is not always necessarily good. It means that it will not protect devices that need a lower current rating, as the overload would not be detected. So, the type of appliance that will be connected to the circuit is vital in determining the size of the fuse.
You can get fuses as low as 3A, 5A, and 13A. However, that is only the beginning; there are many other options for you to consider.
As a general rule, appliances with rewirable plugs will have a fuse of 3A until a device is more than 700W in terms of power rating. If it goes over 700W, a 13A fuse is recommended.
Take note that some devices, such as motors, will have a higher initial current, also called inrush current, when it is turned on. This means the supply current will be higher than the rated current. This means it needs a specific type of fuse that can work with this variation without unnecessarily blowing.
Applications of Fuses
Fuses have so many applications. Many devices we use daily come with fuses. Here is where to expect to find a fuse.
- Many devices can be used in homes. Examples include TVs, refrigerators, and other common household appliances.
- Automobiles such as cars and motorcycles electrical systems also need fuses to prevent chances of short circuits and overloads.
- Industries need fuses for their industrial machinery, power systems, and motors.
- Fuses are also used to protect power systems such as transformers and power lines from overcurrent, short circuits, etc.
So long as circuit protection is necessary, expect a fuse or related device will be in place.
How to Choose the Right Fuse for an Application
Choosing the right fuse is generally easy, but sometimes you have no idea where to start. Let us help you make the right decision. Here are the factors you should consider when picking a fuse for an application.
1. Understand the Application
Look at the fuse’s voltage and current rating. These are vital for ensuring you always get it right. For example, the fuse’s current rating should be slightly higher than the normal operating current. This prevents unnecessary tripping.
The load type is also important. Is it a resistive, inductive, or capacitive load? Such characteristics can affect how a fuse is selected.
2. Temperature Derating
This is an important factor as it affects the fuse reliability. As the appliance works, its temperature is expected to rise and fall. As such, the fuse should be able to keep up with changes in temperature and still work correctly.
For U.S. standards, fuses must be tested for current rating at a controlled temperature of 25 degrees C. So, the current rating will be derated by 25% for the best operation to avoid blowing unnecessarily.
3. Melting Integral
Melting integral is loosely translated as current squared times time. The time here means the surge length. It simply means that the heat generated across the fuse in case of a surge does not have sufficient time to jump to the external circuit.
This factor determines the energy needed to melt or blow a fuse element. If the melting integral is high, then the fuse takes longer to blow. It is recommended to get a fuse whose melting integral is greater than the inrush current energy.
4. Fuse Type
Depending on the device, a fuse type will be recommended. For example, AC devices need AC fuses, and DC devices need DC fuses. It can even get more specific where you have time-delay fuses, slow-acting fuses, and fast-acting fuses. It is simply important to choose according to the application.
Signs That Your Fuse is Blown

A visual inspection of a fuse can help you know if it is working or not. Look for a broken filament. If there is a gap in the fuse, it means that the filament has melted, blowing the fuse. Also, look for burn marks or other physical damage. They show that the fuse is blown.
Loss of power is often a good indicator that the fuse has blown. If the lights are out, check the fuse first. If that is the case, simply replace the fuse and turn on the lights again. The same applies when trying to troubleshoot why your vehicle is not starting or the headlights are not coming on.
A burning smell is another good indicator of a blown fuse. If you can smell something burning near the fuse box, check the fuses with a car fuse tester to see which one is blown.
Before the burning smell, you may also hear a popping sound. This is a common sound that accompanies the blowing of a fuse.
Some vehicles might indicate there is a blown fuse on the dashboard to help you know about it and start the replacement process.
How to Test and Replace a Fuse

Now that you know how to tell if a fuse is blown, we also want to look at how to test and replace one.
Other than the visual inspection, the best would be to test the fuse with a multimeter to find out which one is blown. Here is the process;
- Set your multimeter to the resistance or continuity mode
- Place a probe on each end of the fuse
- A good working fuse shows continuity. This is where the multimeter beeps or shows a low resistance reading.
- In the case of a blown fuse, there will be no beep or a high resistance reading showing no continuity.
Once you establish the blown fuse, it is time to replace it. Simply pull the fuse out of its socket and replace it with one that has a similar rating. This is very important to ensure the fuse continues working as expected.
Test the circuit to see if the fuse is working, and you should be good to go.
How to Maintain Fuses
Maintenance of fuses does not involve doing much. The first step would be regular inspections. Fuses can wear, get damaged, or corrode with time. Make sure that you replace such fuses in time.
Look at the fuse’s fit. Does it sit properly in the fuse holder? Use a piece of paper as a simple tool to test the fit. If the paper easily slides between the fuse and the clip, it shows improper contact.
Always replace the blown fuses with the correct fuse replacement. Some people tend to replace the blown fuses with any conductor, such as foil. This is not good as it will not provide any protection for your circuit.
Conclusion
Fuses remain key in helping protect circuits. You should use the right fuse depending on the appliance. It is vital to always replace blown fuses with the same one that is supposed to be used. This ensures proper protection against overcurrent in the circuit. Also, buy from top brands which at least assure you of the best performance for fuses.


