TOP253PN Datasheet & Pinout | PDF
- Output Isolation: Isolated
- Topology: Flyback
- Fault Protection: Current Limiting, Over Temperature, Over Voltage
- Package: 8-PDIP-C
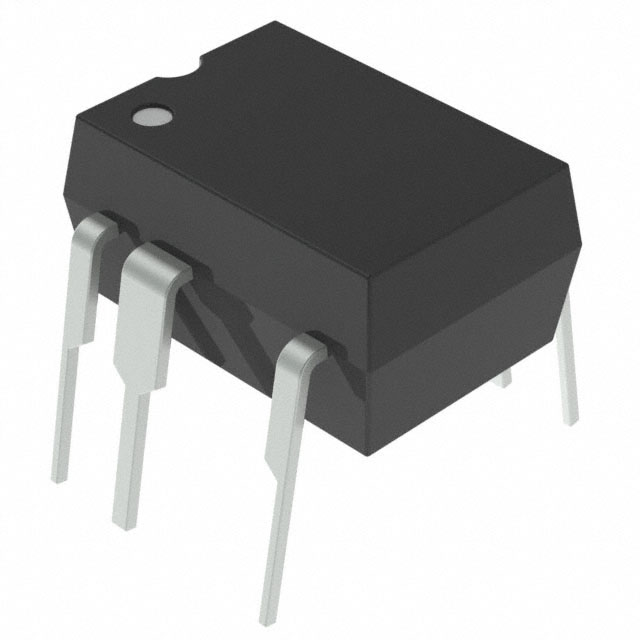
TOP253PN
TOP253PN Pinout


TOP253PN is an off-line switching power supply chip. Mostly used for PWM control, oscillator, thermal shutdown circuit. The following is the pin wiring diagram.
| Pin | Designation | Descriptive |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | M (Multi-function pin) | Multi-function interface for external circuit connections. |
| 2 | C (Control pin) | Connect the output of the optocoupler to receive the control signal. |
| 4 | D (Drain pin) | Connect the primary windings of the transformer and voltage conversion. |
| 5-8 | S (Source pin) | Grounding or other component connection. |
Note:
Pin 3 is not present. A notch is left to indicate this location, primarily to make it easier to distinguish the order and orientation of the pins.
TOP253PN Equivalent
This is a table of equal types for TOP253PN
| Picture | Name | Company | Operating Frequency | Input Voltage Range | Package |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
TOP253PN | Power Integrations | 66kHz | 85-265VAC | eSIP-7C/DIP-8C |
 |
BPA8505D | Shenzhen Huadrill Electronic Co. | Adaptive, up to 45kHz | 85-265VAC | SOP-7 |
 |
LNK305DG | Power Integrations | 66kHz | 85-265VAC | eSIP-7C |
 |
PN8016 | Chilsin Microelectronics | PFM control with variable frequency | 85-265VAC | SOP7 |
 |
PN8034CSSC-R1 | Chilsin Microelectronics | PFM control with variable frequency | 85-265VAC | DIP-7/SOP-7N |
 |
TNY274PN | Power Integrations | 132kHz | 85-265VAC | DIP-8 |
Note:
The best replacement is the LNK305DG, which has the same operating frequency of 66kHz as the TOP253PN, the same input voltage range of 85-265VAC, and a similar package shape as the TOP253PN. When using PN8016 and PN8034CSSC-R1 as replacements, the main issue to consider is the package. When using BPA8505D and TNY274PN as replacements, circuit and electronic components may need to be modified due to its different operating frequency from TNY274PN. Avoid damage to electronic components. PFM control with variable frequency: Adjust the output by changing the frequency of the switch pulse while keeping the pulse width relatively constant. For example, just like controlling the water output of a faucet, the pulse frequency is like the number of times the faucet is turned on and off, and the pulse width is like the length of time the water flows out each time the faucet is turned on and off. PFM control is the process of adjusting the water output by varying the number of times water is released to control the total water output. The advantage of PFM control is that it can save electricity under light load and flexibly adjust the output; The disadvantage is that the frequency variation range is limited, which can easily generate electromagnetic interference, and the control is relatively complex.
More Like This
Also Add to Cart
MPQ3367GR-AEC1-Z
Monolithic Power Systems Inc.
PT4115
UMW
PT4115
EVVO
TPS92665QPHPRQ1
Texas Instruments
LT8355IUFDM-1#WPBF
Analog Devices Inc.
MP4056GS-Z
Monolithic Power Systems Inc.
TPS929240QDCPRQ1
Texas Instruments
HMC765LP6CE
Analog Devices Inc.
SI5347A-B-GM
Skyworks Solutions Inc.
HMC807LP6CE
Analog Devices Inc.