BD140 | transistor datasheet | PNP transistor | circuit diagram onsemi
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Current-Collector(Ic)(Max): 1.5 A
- Voltage-Collector Emitter Breakdown (Max): 80 V
- Vce Saturation(Max)@IbIc: 500mV @ 50mA, 500mA
- Price: inquiry
How the BD140 transistor works:

BD140 pinout Diagram
Transistors are current controlled devices and therefore need a little current to switch them on. For the BD140 triode, this base current is less than 10mA because the BD140 is a PNP triode, which conducts when the base is grounded and cuts off the transistor when a positive voltage is applied to the base.
The following simulation circuit shows how the BD140 transistor behaves when the base of the transistor is grounded and connected to a 12V supply.
The specific performance is as follows:
- the transistor conducts when the base is grounded, allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector
- when a positive voltage is applied to the base (12V in this example), the transistor cuts off
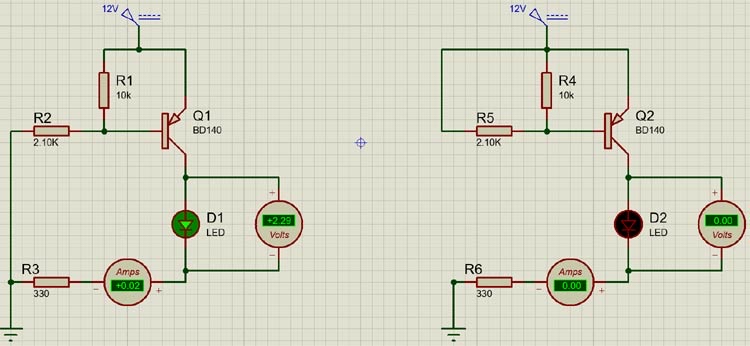
BD140 Circuit Diagram
When we switch on the transistor by grounding the base, the transistor will remain switched on until the voltage at the base of the transistor exceeds the base-off voltage, then the transistor will be switched off. For this transistor, the on voltage is between 0.7 – 0.9V and the base of the transistor must not be in a suspended state, otherwise false triggering may occur, leading to problems in the driver circuit. To avoid this problem, we can add a 10K pull-up resistor, such as R4 in the example, a 10K resistor is used to pull up the base of the transistor to VCC to use.
We need to be careful when designing circuits using the BD140 triode:
1.Base circuit with appropriate current limiting measures, such as base series connection of a 10 resistor (the specific size and circuit design)
2.Select the appropriate pull-up resistor value according to the specific application (typical value is 4.7K or 10K).
3.Applications that require high currents to flow need to take into account the need for heat dissipation, so the maximum power consumption and maximum junction temperature of the transistor should also be taken into account.
Key Benefits of the BD140 Transistor
High Power: The BD140 power transistor has a maximum collector current of 1.5A and a maximum collector voltage of 100V.
Low Loss: The BD140 power transistor has a loss coefficient of less than 0.1%, which can minimises the energy loss in the circuit and improves the efficiency of the circuit.
High-speed switching: The switching speed of BD140 power transistors can reach 100ns, which can meet the needs of most industrial control systems for high-speed switching.
High Frequency: BD140 power transistors have a maximum transition frequency of 190MHz with good frequency characteristics.
Why Use BD140?
The BD140 triode is a versatile and reliable triode that balances performance, efficiency and size. Its excellent performance makes it the first choice for engineers and designers in projects such as power control, audio amplifiers and motor drivers.
More Like This
Also Add to Cart
MMBT2222A
HY Electronic (Cayman) Limited
MMBT3904
HY Electronic (Cayman) Limited
MMBT2907A
HY Electronic (Cayman) Limited
TIP41C
Rochester Electronics, LLC
PMBT3904,215
Rochester Electronics, LLC
TIP120
Central Semiconductor Corp
TIP36C
Central Semiconductor Corp
TIP35C
Central Semiconductor Corp
TIP3055
Central Semiconductor Corp
TIP2955
Central Semiconductor Corp


.JPG)







.jpg)